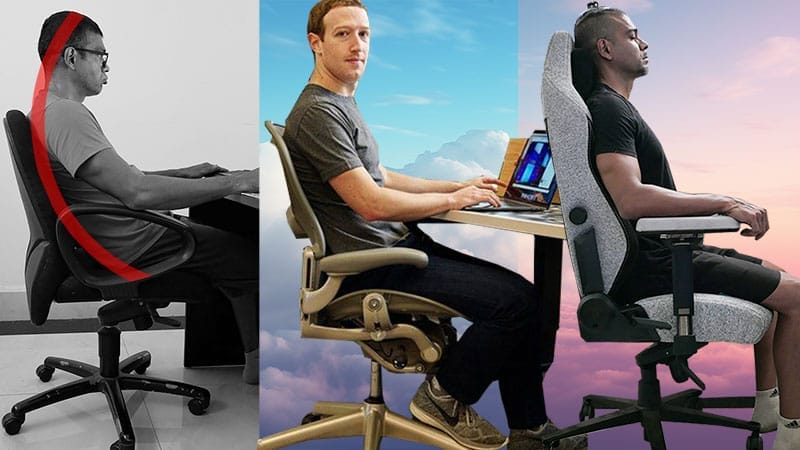
People new to ergonomic seating often wonder about gaming chair vs office chair similarities and differences. In 2024, the biomechanical evidence is clear. Standard, non-ergonomic office chairs can cause back pain and fatigue. Gaming chairs and ergonomic office chairs both qualify as ‘ergonomic’. Ergonomic seating keeps the spine in a healthy alignment. This helps users sit comfortably — with more energy and sharper focus. Read this simplified office chair vs gaming chair explainer before you start shopping for a desk chair.

It’s common to feel exhausted after a long plane flight. Long sitting periods on a fluffy sofa or basic, non-ergonomic office chair will also wear you out. NASA discovered the reason for this — in outer space — in 1973.
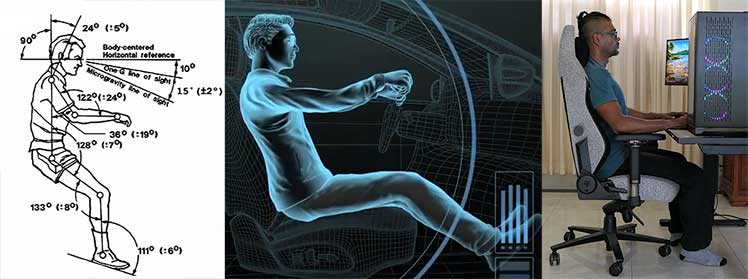
When relaxed in zero gravity, Skylab astronauts often fell into neutral body postures. These align the spine in a healthy manner to hold the spine upright against gravity. As a result, the upper back muscles can relax — rather than over-exert.

The problem on Earth is a stronger gravitational pull. Standard office chairs hold your buttocks up against gravity, but not your spine. Sitting forces back muscles to work harder. Once they tire, the spine sags into an ugly slouch.
Physical & Mental Deskwork Problems
Modern desk workers computing on non-ergonomic seating face a dual assault on the spine. Seated desktop computing flattens the lower back curve. Excessive mobile computing rounds the upper back and neck. This combination distorts the alignment of a healthy spine.
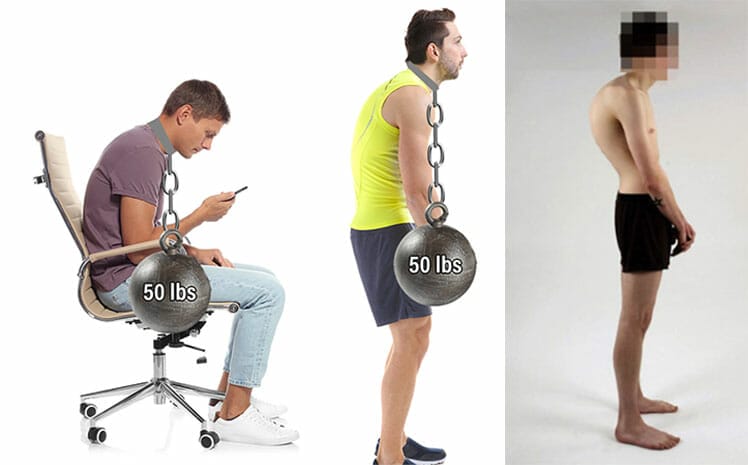

In a healthy standing position, the lower back curves inward with a 25-45° angle. Sitting without support flattens that curve by half. Then, back muscles must work harder to hold the spine upright.
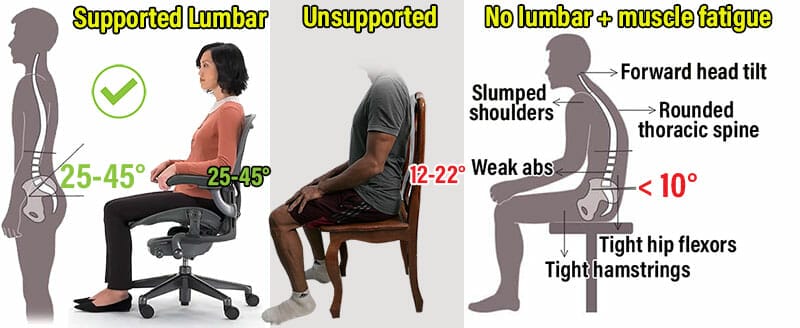
When back muscles fatigue, posture falls apart. Adding mobile computing stresses makes things worse. The average adult now spends over three hours per day using a cell phone.

The harm caused by mobile and desktop computing both count as types of physical technostress. These lead to productivity-killing mental technostress issues like brain fog and depression.
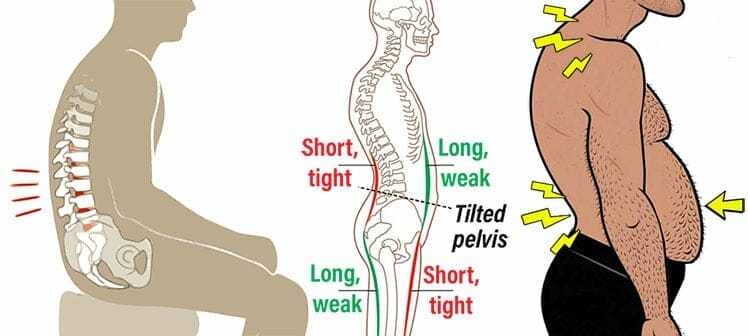
Here are the most common Musculoskeletal disorders caused by poor posture habits:
- Unsupported sitting: tightens the lower back, curling the hips forward.
- Forward neck tilt: bends the upper spine more severely.
- Anterior pelvic tilt: tight lower back + bent neck = tilted hips.
- Chronic pain: back, neck, and shoulder pain + migraines are common.
Modern Desk Work Maladies
Full-time desk workers sitting on standard office chairs risk their physical and mental health. Unhealthy sitting in a standard office chair causes spinal misalignments and pain.

Bodies suffering from chronic pain move less. That ramps up the risk of diabetes, hypertension, weight gain, depression, cancers, and worse.

These statistics illustrate the plight of the modern desk worker:
- Sedentary: Americans spend 55% of their waking time (7.7 hours a day) engaged in sedentary behaviors; Europeans spend 40% of their leisure time watching TV.
- Back problems: Millennials (27-42 in 2023) generate 22% more back disorder ER visits than other generations.
- Obese: Cancer Research UK warns that 70% of British Millennials will be obese by the time they reach middle age.
- Brain fog: Obesity reduces the grey brain matter that sends and receives information. As a person gets fatter, their cognitive functioning slows. That leads to short-term memory loss and learning difficulties.
- Depressed: the number of antidepressants prescribed in the UK has increased by 35% over the past 6 years(2).
Gaming Chairs Vs Office Chairs 2024
A consensus on the healthiest way to sit for long periods has been around since the early 1990s. Dynamic neutral postures align the spine to reduce strain on surrounding muscles.
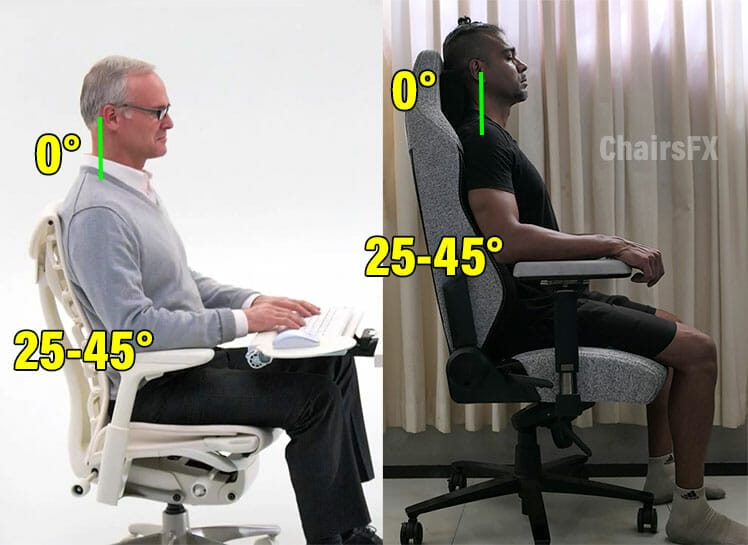

Sitting neutrally, users enjoy long periods of comfortable, stress-free computing. A textbook neutral posture yields two angles: a 25-45° lower back curve and a 0° neck tilt.
To support these angles, any chair that qualifies as ‘ergonomic’ needs three adjustable components:

- Adjustable lumbar support: maintains a healthy lower back curve.
- Adjustable armrests: provide extra bracing to hold the torso upright.
- Reclining backrest: enables movement and custom back angles. Reclines between 100-130° — with a supported lumbar curve — exert the least spinal disc pressure.
The standard (non-ergonomic) office chair lacks these adjustable components, rendering it outdated for these times. Two other ergonomic options remain viable:
- Ergonomic office chair: strict mid-back neutral support that keeps users upright at all times.
- Gaming chair: versatile full-back neutral posture support plus casual lounging options.
Standard Office Chair
When office chairs became ubiquitous in the early 1900s, knowledge about healthy sitting biomechanics was non-existent. As a result, these chairs are designed to be cheap and durable, rather than supportive.

Circa 2023, standard office chair functionality is the same as it was back in 1915. Like the early pioneers, modern versions let you adjust the seat height, rock the chair, or lock the seat in place.
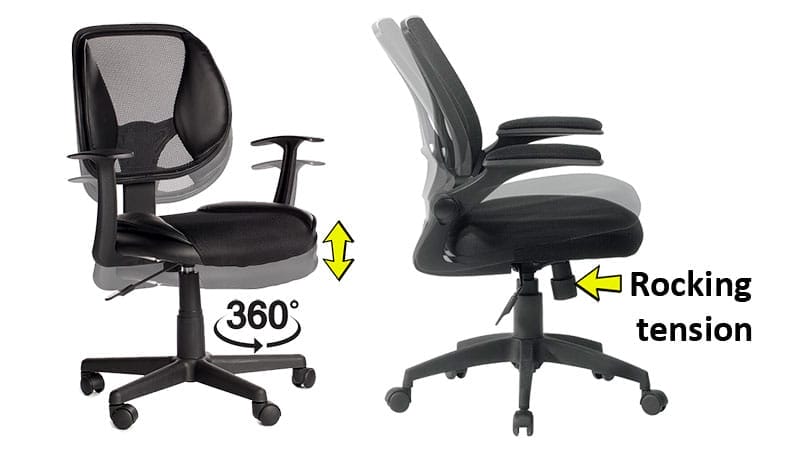

The low price and rugged durability keep standard office chairs in place at many companies. That’s partially why around 22% of the global population (1.7 billion) suffer from musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs).
Predictably, lower back pain is the leading cause of disability in 160 countries(3). Other common MSDs:
- Chronic fatigue: a misaligned spine drains energy by forcing muscles to work harder.
- Migraines: forward head posture stresses neck muscles until pain explodes in the brain.
- Wrist disorders: 4 million Americans suffer from carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Neck pain: the fourth-leading cause of disability in America.
- Shoulder pain: causes around 4.5 million USA doctor visits per year and $3 billion in health costs.
Learn more: Why Non-Ergonomic Office Chairs Are Bad For Your Back
Mid-Back Ergonomic Office Chair
The mid-back ergonomic office chair arose in the early 90s in response to the rise of personal computing. ‘Ergonomic’ means ‘adjustable’. These chairs stack adjustable features on top of a standard office chair build.

These features support desktop computer users into neutral sitting positions. A reclining backrest and lumbar support keep the spine aligned. Adjustable armrests raise arms to the height of a keyboard and mouse. This combination takes massive pressure off the spine.
- Reclining backrest: angles between 100-130° reduce pressure in the lower spine.
- Adjustable lumbar support: maintains a healthy lower back curve.
- Adjustable armrests: absorbs arm weight, reducing neck and shoulder strain.
Standard Office Chairs Vs Ergonomic Office Chairs
Standing with good posture produces a healthy lower back curve of 25-45°. Unsupported sitting flattens that curve by about half. That forces back muscles to work harder at holding the torso upright. As muscles tire, postural integrity collapses.
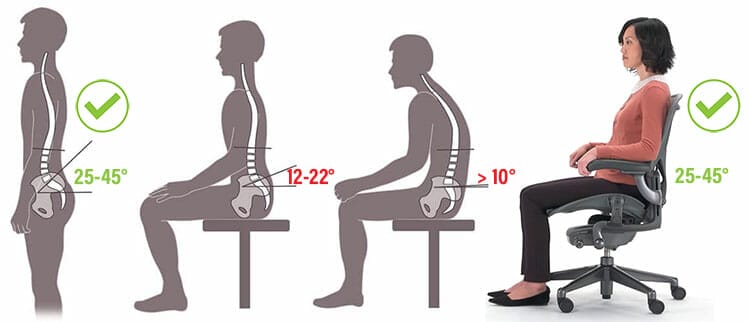
This explains why good posture collapses when using non-ergonomic office chairs for long periods.

In contrast, an ergonomic chair with adjustable lumbar support, adjustable arms, and a reclining backrest can keep the spine healthily aligned. For example, sitting with good form in a Steelcase Series 1 chair is easy and intuitive.
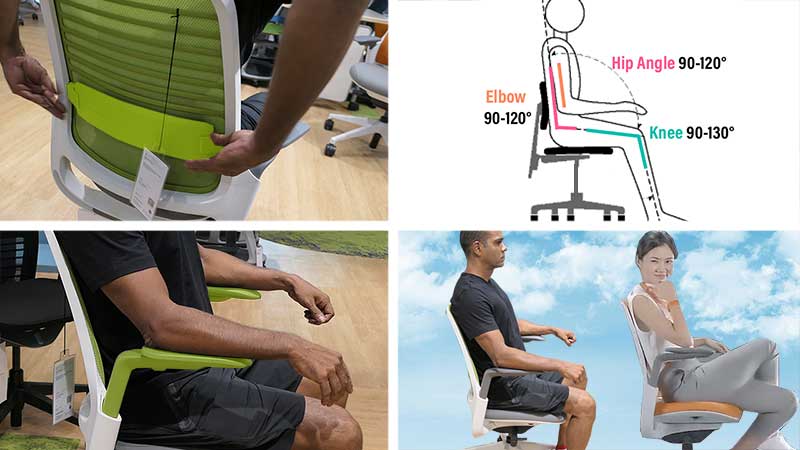

Adjust the seat height. Then, tuck your hips, plant your feet, and use the lumbar support to preserve your lower back curve. For extra support, adjust the armrests until your shoulders feel relaxed.
Then, sitting upright for long periods becomes almost effortless. The process works the same with any chair having adjustable lumbar + armrest + recline features. Learn more:
Full-Back Gaming Chair
The full-back, racing-style gaming chair is 17 years old in 2023. The first model debuted in 2006. In the early days, these were often dismissed as gimmicky scams designed for dumb gamers.

Fast-forward to the modern era and the humble gaming chair has blossomed. Today, it’s a viable option for both gamers and desk workers, offering two advantages over ergonomic office chairs. The first has to do with headrests.
Ergonomic office chairs are only designed to support your neck in reclined positions. Most are not depth-adjustable. When you sit with an upright 100-110° recline, office chair headrests push the neck forward.
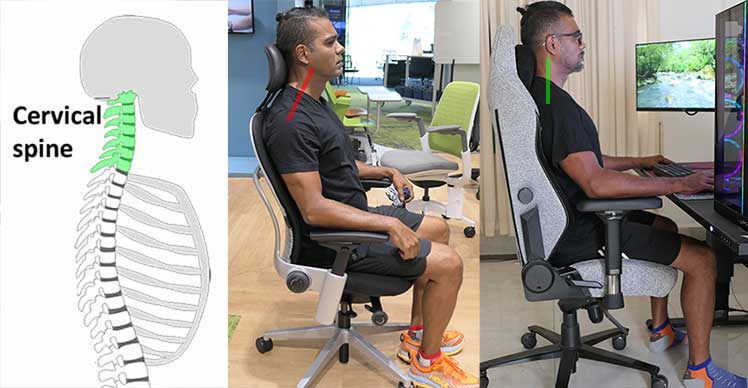
In contrast, gaming chair headrests support good neck posture in both reclined and upright positions.
More Versatile Than Mid-Back Ergonomic Chairs
Gaming chair recline functions also provide more versatility. The best ergonomic office chairs only recline between 100-125°; gaming chairs recline deeper (usually up to around 165°).

Deeper reclines make full-back gaming chairs useful for deskwork, gaming, mobile computing, and even napping. A deeper recline range with full-back support is also useful for the overweight and obese.
Neutral Posture Support For Obese Sizes
Most with a BMI over 30 suffer from unusually weak spines. That can make sitting up straight in a mid-back chair difficult. Fortunately, when you set a full-back gaming chair recline to 110° or deeper, gravity takes over.

Then, instead of your back muscles doing the work, the tall backrest, lumbar support, and body weight support your spine instead.
Healthy Ergonomics For Desk Workers
With proper technique, gaming and ergonomic office chairs both support textbook neutral postures. In both cases, users need to tuck their hips, plant their feet, and keep their lower back curve supported.

I’ve tested all of the world’s best gaming and ergonomic office chairs. In my experience, any model with adjustable lumbar + arms + recline features can provide the physical support you need. Learn more:
Office Vs Gaming Chair Aesthetics
Both standard and ergonomic office chairs are designed for corporate environments. Most come in conservative neutral colors with limited recline ranges and mid-back designs. In an office, mid-back chairs make it easier for managers to monitor staff while they work.

On the flip side, gaming chairs provide neutral sitting support beyond the confines of office norms. Tall backrests provide full-back support.
Beyond cradling your entire spine, this provides a brilliant privacy shield against prying eyes. As well, gaming chairs come in both muted and wild color schemes.

If using one in an office, choose a conservative style to blend in with the crowd. If working from home, there’s no limit. You can choose bright color schemes, striking embroidered ones, soft pastels, and plenty more.
Pros And Cons Of Each Seating Type
For full-time computing in the multi-device era, standard office chairs are out of the equation. That leaves two viable ergonomic seating options on the table.

See our Gaming Chair vs Ergonomic Office Chair article for a deep dive into the differences. Find below a quick summary:
Standard Chair: Cheap But Non-Ergonomic
A standard office chair lets you adjust the seat height, rock the seat, or lock it. It has non-adjustable armrests and no adjustable lumbar support. Despite the lack of support, many companies prefer these for their low price and rugged durability.

But from a user perspective, computing full-time on a non-ergonomic chair is bad enough. Stacking 3+ hours of text neck mobile computing on top of that is fertile ground for a musculoskeletal disaster.
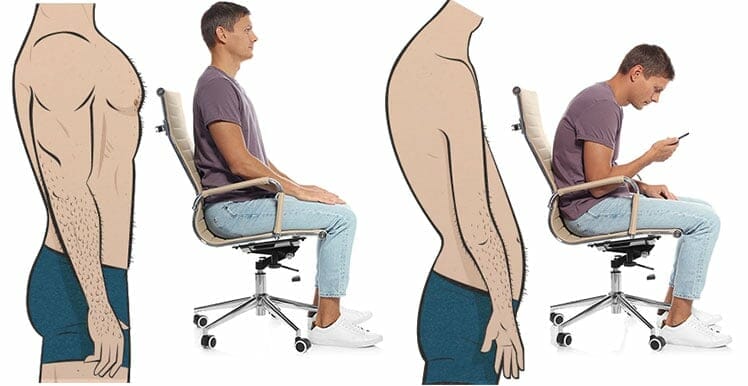
The human body is not designed to sit for long periods. Without ergonomic support, that sets off a chain reaction. First, the lower back curve flattens. Then, the hips tilt forward. That combination curves the upper back and neck into an ugly forward slouch.

If you are working full-time on a non-ergonomic chair right now, these symptoms probably fit you like a glove:
- Muscle and joint pain: misaligned muscles and joints must work harder. Over time, that manifests as chronic pain in the back, shoulders, neck, arms, or legs.
- Chronic headaches: a forward head posture increases stress on joints and muscles in the upper neck. Pain begins at the base of the neck and then creeps upward. The more you slouch, the worse the pain.
- Chronic fatigue: imbalanced posture stresses body parts that are not meant to bear weight. That burns more energy until muscular fatigue sets in. Prolonged fatigue worsens imbalances, forcing the body to work even harder.
- Slower digestion: poor posture restricts blood flow and compresses the intestines. As food moves slower through the system, bloating and constipation arise.
- Poor circulation: clogged circulation from postural misalignments cause varicose veins (especially in women).
- Depression: many studies show a correlation between poor posture and negative vibes. People who sit upright tend to be more alert, positive, and energetic. Those who slouch tend towards apathy and negative thinking.
Ergo Chair: Supportive But Restrictive
“The more mechanically distorted a person is, the less energy available for thinking, metabolism, and healing.”(4) The reverse is also true. Sitting properly in a good ergonomic chair takes massive pressure off of the back, neck, and upper body.
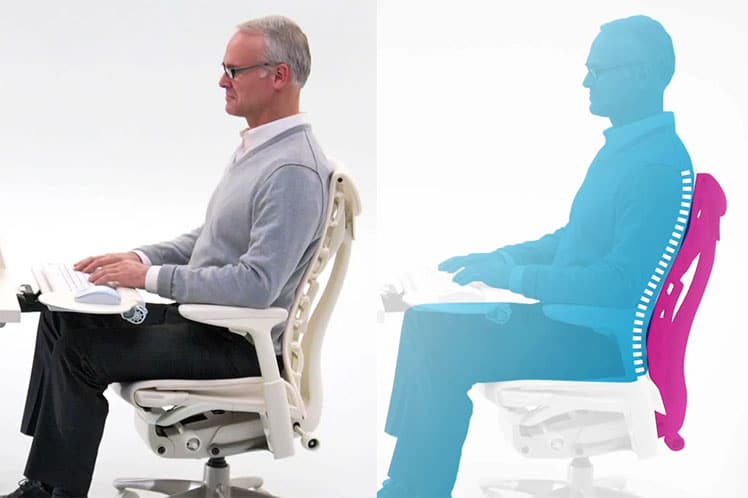

It also opens up the rib cage, boosting oxygen levels by up to 30%. That enables faster processing in the prefrontal cortex (cognitive control center). As a result, workers become more alert and energetic, with a higher level of brain activity(5).
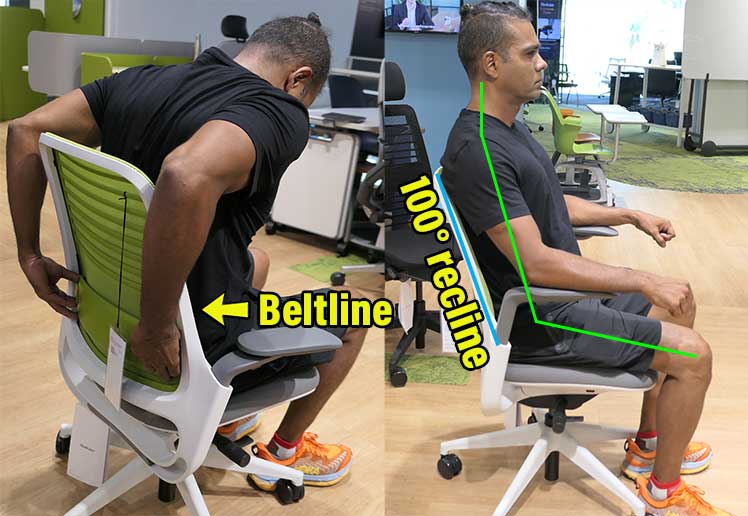
Summary of good posture benefits:
- Fewer headaches: good posture reduces the neck tension that causes migraines.
- Reduced musculoskeletal stress: sloppy sitting misaligns the hips and spine. That stresses joints and surrounding muscles.
- More oxygen: good sitting posture opens the chest cavity, increasing oxygen intake.
- More energy; sharper focus: an aligned body works muscles efficiently. That leaves more energy for brainwork.
- Improved digestion: efficient body mechanics speed metabolism and the passage of waste.
Ergonomic Office Chair Downside
Most mid-back chairs have limited recline ranges that keep users in ‘working postures’. Indeed, forcing staff into crisp upright positions all day long works well in office settings.

But when working from home, there’s no need to stay sharp and formal at all times. That’s the big downside: if you want to kick back and relax, your ergonomic office chair won’t let you!
- Straightforward, reliable posture support
- Easy to use
- Prevents sloppy sitting habits
- No deep recline functions
- Sitting upright all the time can feel restrictive
Gaming Chair: Versatile But Easily Misused
The full-back gaming chair is a viable alternative to the ergonomic office chair. Users can enjoy a similar level of neutral sitting support, plus plenty of extras.
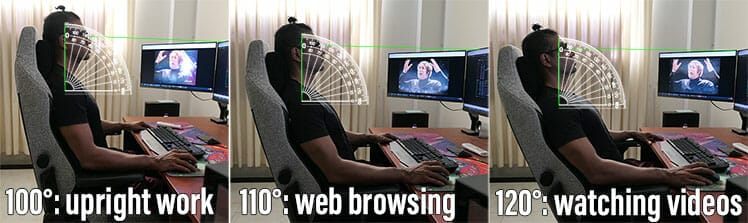
In a work-from-home setting, deep recline gaming chair functionality provides all-day sitting support. Beyond deskwork, users can kick back to relax, watch a movie, use a mobile device, or even take a nap!
In an office setting, gaming chairs are also trending, especially in Asia. China in particular has a strong nap-at-noon working culture(6). Western companies like Google and NASA are also adopting this practice by integrating sleep pods into offices.

Thus, a gaming chair in an office setting makes perfect sense. The ergonomic functionality supports long periods of deskwork with good posture. At noon, a deep recline provides the perfect spot for a noontime nap!
Downside: Freestyle Sitting Is Easy To Abuse
Unlike strict office chairs, gaming chairs don’t force you to sit straight. This freedom is a big point of appeal — but also a major drawback.

Muscles adapt to frequently-held positions(7). So the longer you sit off-kilter, the more the body will adjust. For instance, if you go overboard sitting with one foot up, muscles will tighten on one side of your body and loosen on the other.

As your body falls out of misalignment, your posture will degrade further. Because of muscle memory adaptation, those postures will start to feel more comfortable than healthy ones!
Then, your only way out is to do a postural reset. That means forcing yourself to sit in a crisp neutral posture (for 2-3 days) until muscle memories adapt.
- Reliable posture support
- Easy to use
- Deep recline + the freedom to sit however you like
- You will need effort and self-discipline to maintain good posture
4 Pillars Of Computing Performance
These days, many top streamers, pro esports players, and even pro chess players rely on ergonomic chairs to help them perform better.

For most, an ergonomic chair doesn’t play a starring role, but a secondary one. For instance, esports powerhouse Team Liquid and chess star Magnus Carlsen both use Secretlab Titan gaming chairs.

Both also use variations of the four pillars of computing performance. These are:
- Nutrition: eating clean foods for consistent energy without sugar crashes.
- Rest and Recovery: give the brain enough time to recharge.
- Physical Fitness: building stronger core muscles helps athletes sit longer without strain.
- Psychological Fitness: forging mental balance to avoid burnout.
As an example, Magnus Carlsen’s fitness program centers around cardio and balance exercises. His coach touts cardio as a good way to foster mental endurance. Balance exercises help Magnus develop a strong core.

With good cardio, a strong core, and a Secretlab Titan chair, he’s able to use endurance as a weapon to crush his opponents.
4 Pillars Of Computing Performance
Testimonial: Gaming Chair Wellness Benefits
I don’t just write about gaming chairs — I use them full-time, as part of my own 4-pillar optimization routine. Back in 2017, I bought my first DXRacer model.

Once I figured out how to sit with neutral postures, my life changed. With the chair supporting good posture, my back muscles didn’t need to compensate. Then, these benefits emerged:
- Able to sit comfortably for longer periods.
- A noticeable boost in energy levels.
- Sharper focus and improved computing productivity.
- Greater awareness of my body postures and immediate surroundings.
- Improved sitting and standing posture.
Benefits Of Having More Energy
The energy boost was the big prize. That taught me how a healthy posture enhances executive brain functions. Located in the prefrontal cortex, this part of the brain controls focus, lateral thinking, self-discipline, and working memory.
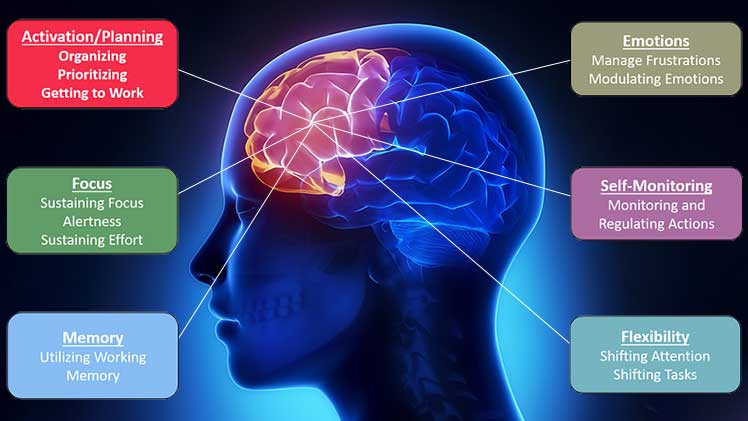
With exhaustion, these functions weaken. With a good ergonomic chair addressing exhaustion, the opposite happens. Having enough energy gives you the power to dabble with the four pillars: clean eating, rest, fitness, and mental balance.
After a few months of adapting to my gaming chair, I found myself brimming with too much energy. I parlayed that into sharpening my lifestyle habits and hitting the gym.
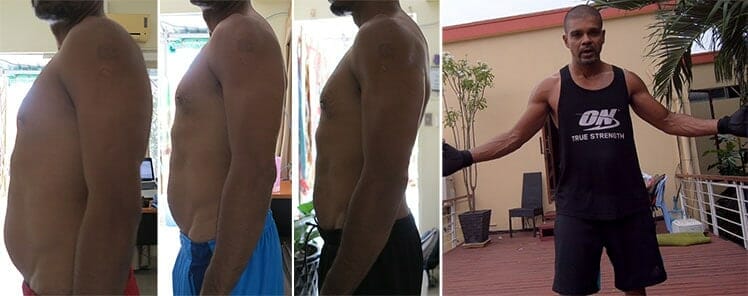
2023 marks my fifth year using gaming chairs for full-time desk work. Over that time, my four pillar habits have evolved:
- Nutrition: low-carb intermittent fasting is my staple; no sugar; limited alcohol.
- Recovery: 8 hours of sleep; 20-minute power naps; deskwork movement breaks.
- Fitness: lifting weights 5 times per week plus daily cardio.
- Psychological: mindfulness, meditation, journaling, visualizations.
In five years, my sitting techniques have also gotten more refined. My original neutral postures were more relaxed. These days, I enjoy sitting in textbook neutral postures with a clean 0° neck tilt.
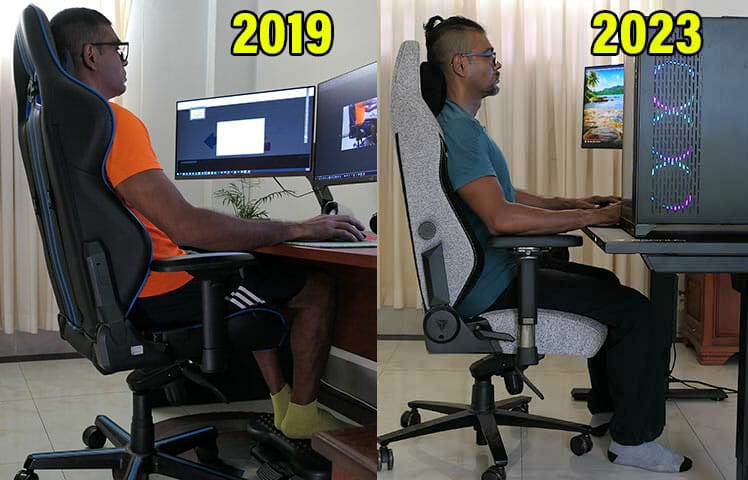

Unlike famous pros like Magnus Carlsen and Team Liquid, I didn’t have anyone coaching me along the way. I’m just a person with a gaming chair. These benefits explain why standard office chairs should seriously consider upgrading:
Conclusion: Gaming Vs Office Chairs
Standard office chairs are bad for your back. These only let you adjust the seat height or rock the chair. These adjustments are not enough to support healthy deskwork over long periods.

Because of this, desk workers worldwide suffer myriad physical and mental problems. The solution to these problems came to us from outer space in 1973. When sat in neutral postures, the spine maintains a healthy alignment. That allows it to hold the body upright with optimal efficiency.
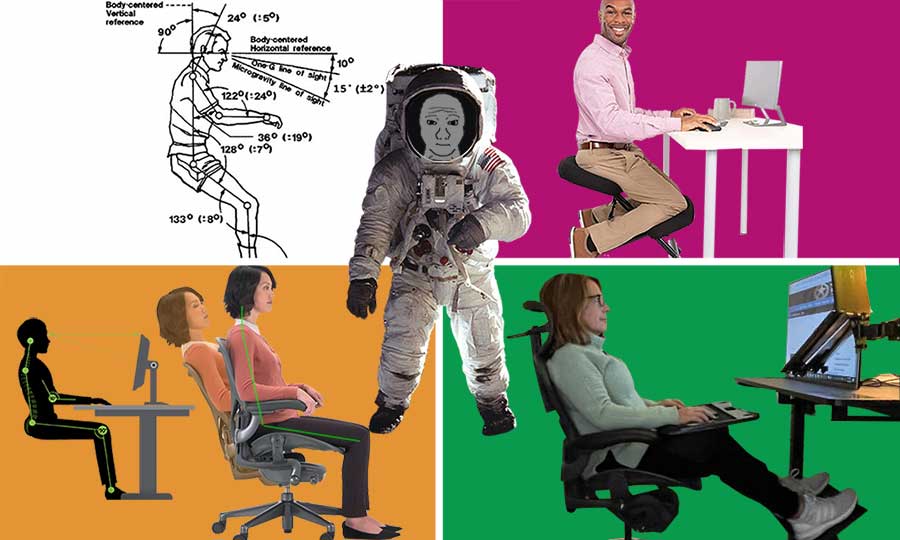

Here at ChairsFX HQ, I’ve been using gaming chairs full-time for over 5 years. Along the way, I’ve also tested out most of the world’s best ergonomic office chairs.

Across the board, they all do an exceptional job of supporting neutral postures. Any model with adjustable lumbar + adjustable arms + a reclining backrest can provide the support that you need.

This includes cheaper ergonomic chairs. These typically come with shorter warranties and fewer luxuries — and the same neutral posture support as pricier chairs!

Bottom line: choose whichever type of fully-ergonomic chair makes you feel happy. For a more specific look at different seating happiness factors, see this head-to-head comparison:
Aeron Vs Titan Evo: Ultimate Gaming Vs Office Chair Battle
Footnotes
- Lee Herrington. ‘Assessment of the degree of pelvic tilt within a normal asymptomatic population’, Manual Therapy, Volume 16, Issue 6, December 2011, Pages 646-648. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1356689X11000816, (accessed August 7, 2023).
- The Pharmaceutical Journal. ‘Antidepressant prescribing increases by 35% in six years’, Mental Health, July 8, 2022. https://pharmaceutical-journal.com/article/news/antidepressant-prescribing-increases-by-35-in-six-years, (accessed August 7, 2023).
- WHO, ‘Musculoskeletal conditions’. WHO Fact Sheets, 8 February 2021. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/musculoskeletal-conditions (accessed 12 March 2022).
- Nema Nyar. ‘Spinal Alignment: The Quest for Stability and Ease’, 16 September 2019. https://himalayaninstitute.org/wisdom-library/why-posture-matters/, (accessed 23 March 2022).
- ‘Proper Posture for Higher Engagement and Cognitive Performance’, 19 September 2017. https://americanpostureinstitute.com/proper-posture-for-higher-engagement-and-cognitive-performance/, (accessed 23 March 2022).
- Hattie Rowan, ‘Naps are good for you. They reduce stress and improve memory and mental health, doctors say’. Health & Wellness, April 21, 20215. https://www.scmp.com/lifestyle/health-wellness/article/3130095/are-naps-good-you-less-stress-better-mental-health-and, (accessed 8 March 2022).
- Erin M. Friend, PT, DPT, CEAS, ‘Poor Posture And Its Effects On The Body’. National Spine Health Foundation, April 8, 2015. https://spinehealth.org/poor-posture-and-its-effects-on-the-body/, (accessed 8 March 2022).




