Are gaming chairs good for your back? Potentially. Full-back gaming chairs and ergonomic office chairs function similarly. Both use adjustable lumbar support, armrests, and a reclining backrest to promote neutral postures. These features help reduce strain by aligning the spine into a healthy position. However, proper usage is essential for optimal results with either type of chair.
A good-quality gaming chair can be a significant improvement over a normal, non-ergonomic office chair. When you sit full-time at a desk without adequate support, your back muscles can become overworked.
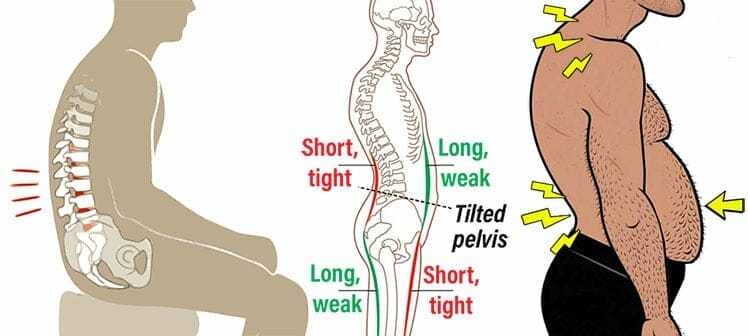
Tired back muscles struggle to hold the torso up against gravity. As a result, the spine curls into a C-shaped slouch. In the short term, sitting with a rounded spine will cause fatigue and lower back pain.

Over the long term, muscles adapt to the way you sit. This type of spinal misalignment causes pain, lethargy, and hormonal imbalances. This may explain why an estimated 80% American adults suffer from anterior pelvic tilt(1).
Gaming chairs are designed to prevent such misalignments by supporting neutral sitting postures. These align the spine so that it maintains a healthy S-curve with a balanced neck and head. However, a chair on its own cannot solve the back pain issue. Users must:
- Adopt neutral sitting postures: plant your feet, tuck your hips deep into the seat, and use your lumbar support to keep your lower back aligned.
- Move while sitting: sitting in fixed postures (even neutral ones) leads to muscle strain. Avoid this by sitting dynamically.
- Take frequent standing breaks: these boost circulation, engage idle muscles, and give your brain a chance to reset.
Grasping these concepts will help you to determine if a gaming chair is right for your needs.
How to Sit In A Gaming Chair Step-By-Step
How Do Gaming Chairs Help?
Gaming chairs use the exact same back support principles as ergonomic office chairs. Both are designed to align the spine in support of dynamic neutral postures.
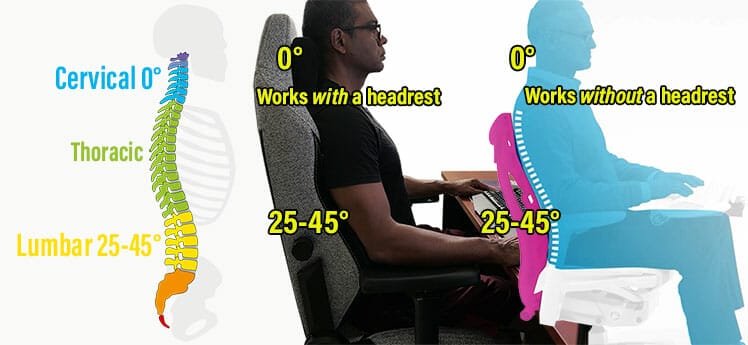
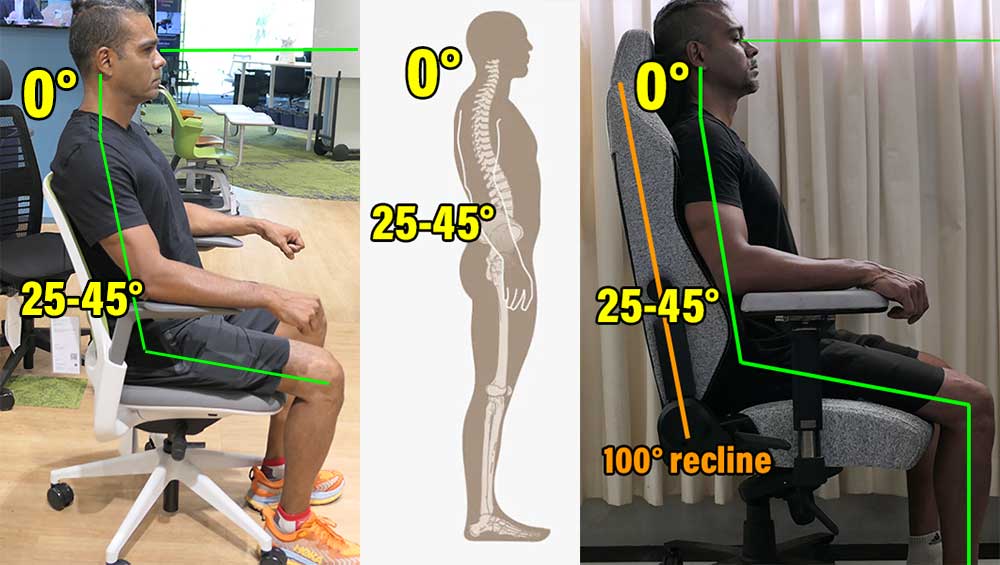
A human spine has cervical, thoracic, and lumbar sections. A textbook neutral posture in either type includes a 0° cervical tilt and a 25-45° lumbar curve.

These numbers align the spine as if it were in a healthy standing position. That best reduces pressure on the nerves, tendons, muscles, and spine while sitting.
To support neutral postures, a chair needs three adjustable features: (2)
- Lumbar support: helps to preserve a healthy (25-45°) lower back curve.
- Reclined backrest: a 100-130° recline (with lumbar support) reduces spinal disc pressure.
- Adjustable arms: support the shoulders; provide extra bracing for the spine.
These help to align the spine and surrounding muscles into optimal positions. But if you start using a gaming chair with poor posture, you’ll need time to adjust.

On day one, sitting straight will start to lengthen and strengthen your muscles. This may feel uncomfortable. But by day five, your spine, muscles, and fascia system will adapt. By day 10, neutral postures should run on auto-pilot as a regular habit.
Then, massive benefits emerge. Here’s the trajectory:
- Standard office chairs: lack the support the body needs to sit for long periods.
- Gaming chairs: have adjustable components that support neutral postures.
- Physical posture benefits: efficient muscle usage leaves more energy for other needs.
- Mental posture benefits: more energy boosts motivation and brainpower.
- Ultimate gaming chair benefit: when comfortable and rested, productivity skyrockets.
Office Chairs Are Bad For Your Back
Standard office chairs have one ergonomic feature: you can adjust the seat height. Otherwise, standard office chairs come with fixed armrests, a fixed backrest, and no adjustable lumbar.

Without the necessary ergonomic features, users develop bad posture habits in these chairs. Over time, these cause many health and mobility issues.
How Basic Office Chairs Harm The Body
When standing with good posture, a healthy lower back curves inward at a 25-45° angle. Sitting straight without support flattens the curve by half(3). A flatter lumbar curve forces back muscles to work harder at holding up the spine.
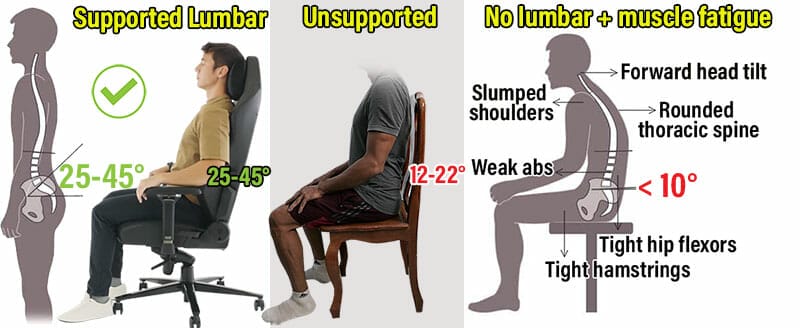
When muscles tire, the back curls into a c-shaped slouch. That flattens the lumbar curve to less than 10°, placing severe stress on lower spinal discs. Over time, pressure builds up in tendons, muscles, and skeletal systems. Then, musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) arise.
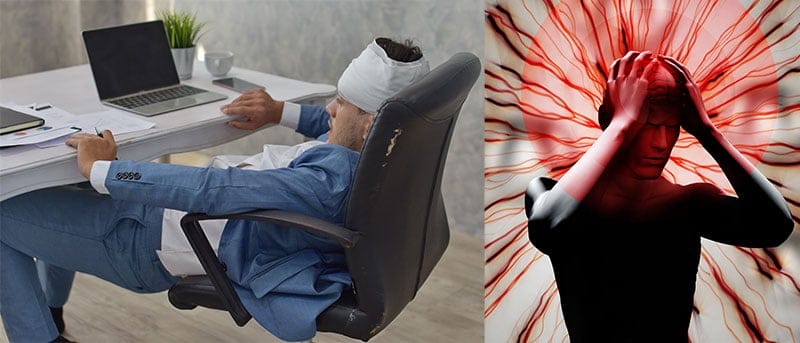
These days, the WHO estimates that around 22% of global adults (1.7 billion people) suffer from MSDs(4). The WHO also counts lower back pain as the leading cause of disability in 160 countries. Other common MSDs linked to sloppy sitting:
- Chronic fatigue: a misaligned spine overworks muscles, leaving users perpetually exhausted.
- Migraines: forward head posture strains neck muscles until pain explodes in the skull.
- Wrist pain: 4 million Americans suffer from carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Neck pain: the fourth-leading cause of disability in America.
- Shoulder pain: causes around 4.5 million USA doctor visits per year and $3 billion in health costs.
- Poor circulation: poor posture clogs blood flow. This causes varicose veins, especially in women.
If you suffer any of the listed symptoms, your basic office chair might be the problem. Learn more:
Gaming Chairs Support Neutral Postures
Like all ergonomic chairs, gaming chairs are designed to support dynamic neutral postures. This is the ergonomic gold standard for reducing spinal stress while sitting. Here’s a recent Secretlab infographic(5) that explains the method:

If you start with poor posture, sitting in clean neutral postures might be difficult — at first. For instance, after over a decade of slouching in office chairs, my 2017 transition to a gaming chair was turbulent.
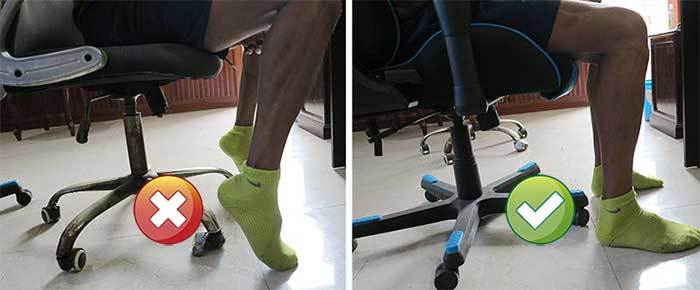
Because my leg muscles were so tight, I had trouble planting my feet on the floor. It took around a week of struggle before my muscles lengthened out.
Muscular Adaptation Posture Therapy
The body adjusts to its most frequently used positions. By forcing yourself to sit in neutral positions, your muscles will adapt to new patterns. Once that happens, the body’s fascia system will adapt(6).
Using these principles, it’s possible to improve your posture by sitting in a gaming chair! With a few days of striving towards neutral postures, your entire body will even out into good postural alignment.

Once the fascia system adapts, neutral positions become your most comfortable. Then, healthy sitting becomes an effortless, ingrained habit. As a bonus, posture benefits gained from healthy sitting will also improve your standing posture!
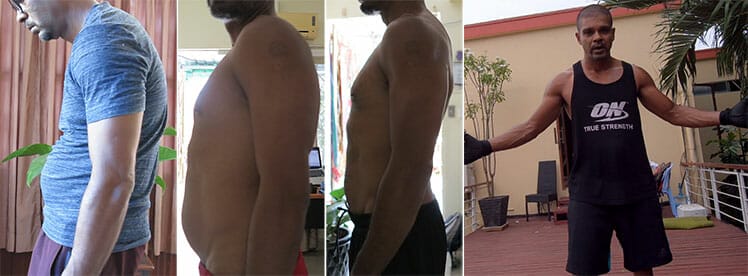
For example, here’s my trajectory over 1.5 years of using a gaming chair. First, I adapted to sitting in neutral postures. That gave me a surge of extra energy, which I put into working out.
Eighteen months later, I was in the best shape of my life — and more productive at work than ever before!
Use Muscle Memory To Form Healthy Ergonomic Habits
Good Posture Health Benefits
The physical benefits gained from using a gaming chair are mainly corrective. Good posture reverses the muscle strain, back pain, and lethargy caused by slouching.
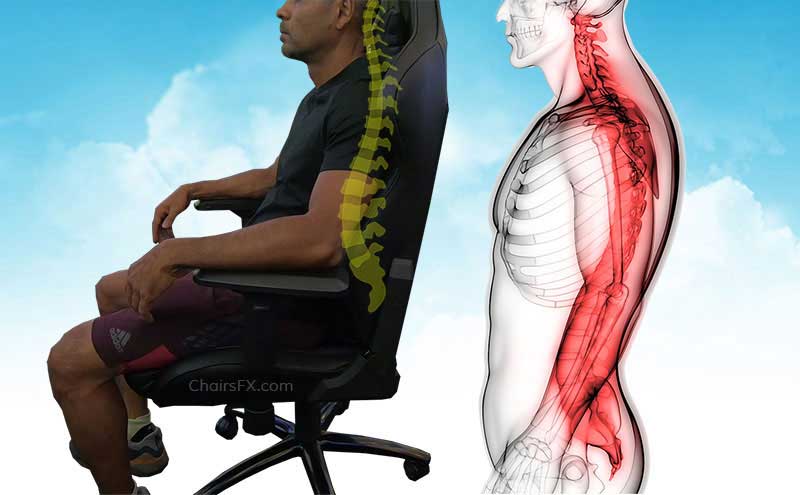
An aligned spine and relaxed muscles let your body operate with efficiency. This is your body’s normal state. If used to life with poor posture, the benefits of good posture might feel life-changing!
- Fewer headaches: good posture reduces the neck tension that causes migraines.
- Reduced joint stress: awkward sitting misaligns the hips. That puts stress on the joints.
- More oxygen: good sitting posture opens the chest cavity and increases oxygen intake.
- More energy and focus: an aligned body works muscles efficiently. That leaves more energy for brainwork.
- Improved digestion: efficient bodily operation speeds metabolism and waste passage.
Good Posture Energizes The Brain
The more out of balance your spine is, the harder your muscles must work to compensate(7). That takes a toll on the brain. In contrast, good posture balances the muscles around the spinal column.

A balanced, aligned body operates with better efficiency. That leaves more energy on the table for cognitive functioning(8). Dr. Roger Sperry (1980 Nobel Prize recipient for brain research) has a famous quote on this topic:
Better than 90 percent of the energy output of the brain is used in relating the physical body in its gravitational field. The more mechanically distorted a person is, the less energy available for thinking, metabolism, and healing.
In simpler terms, ninety percent of all brain energy output goes to supporting an upright posture. The remaining 10% powers thinking, metabolism and healing. With the help of a gaming chair, it’s possible to ‘hack’ this ratio.
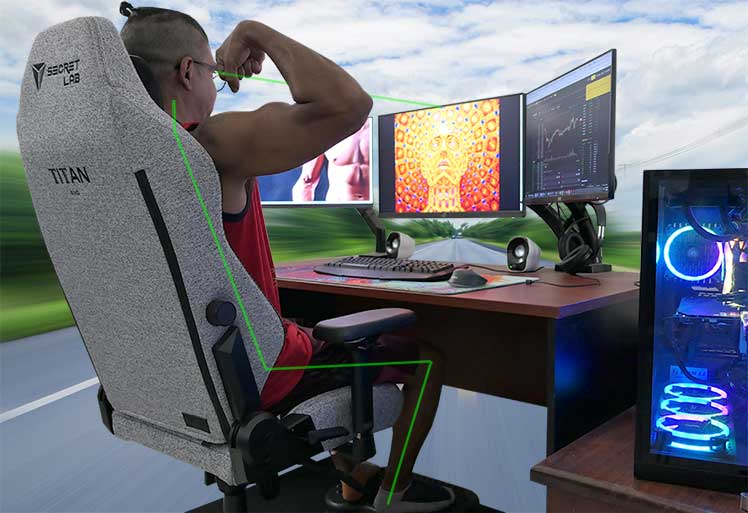

Using one will remove a huge amount of pressure off of the back, neck, and upper body. With more energy to play with, you’ll feel a lot more focused.
Energized Brain Supercharges Productivity
Slouching overworks muscles, burning energy that could instead power the brain. This is counterproductive to “working” at a computer.
In fact, many studies show that poor posture amplifies apathy; sitting straight makes people more alert. There’s a scientific explanation.
The human brain has billions of neurons and trillions of synaptic connections. These fuel processing, memory, and information transmission. Sitting with slumped shoulders compresses the rib cage. That reduces oxygen intake by up to 30%.
Less oxygen slows computational speed in the prefrontal cortex(9). That is the “thinking” part of the mind. As the slouching body compresses, so does the mind.
That’s why people who slouch often suffer from brain fog and an inability to concentrate. In sharp contrast, neutral sitting makes people more alert, with a higher level of brain activity.
Gaming Chair Back Support Features
All types of ergonomic chairs support neutral postures with three core features. Like ergonomic office chairs, a gaming chair’s armrests, lumbar support, and backrest recline provide the magic.
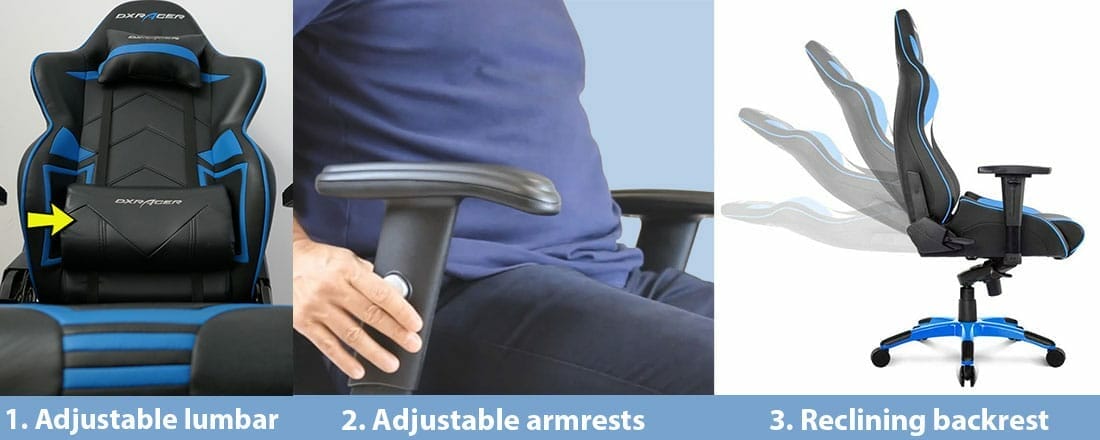
Combined, these components make it easy for users to adopt dynamic neutral postures. However, slight misconfiguration can throw things off.
This video explains how everything should work to effectively support the back:
Here’s a closer look at the gaming chair features that support good posture while you sit:
Adjustable Lumbar Support = Straight Back
In all types of gaming chairs, an adjustable lumbar is the key to sitting up straight. When standing, a healthy lumbar curve is between 20-45 degrees(3). When sitting, applying pressure to the lower back helps to maintain a healthy standing curve.
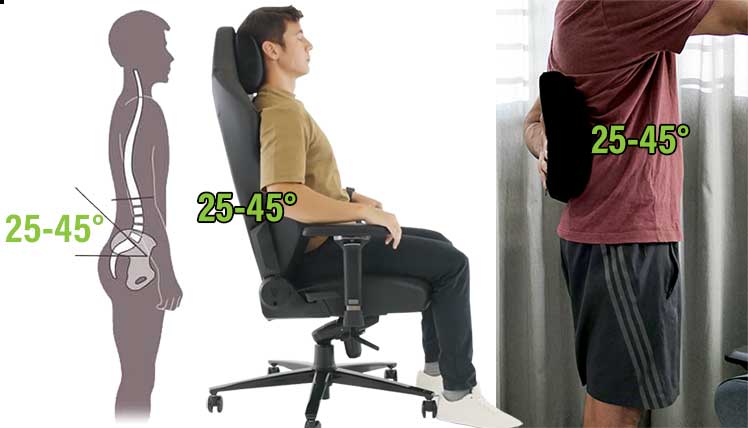

Many first-time gaming chair users struggle with this part. Setting the support too high or low will curl your hips forward and promote slouching.

As a rule, always set your lumbar pillow a few inches higher than the seat. The average adult spine is around 30″ long for men and 24″ for women. The typical man should position his lumbar support around 7.5″ above the seat; a woman should aim for 5.5″ higher.

As technical guidance, this famous study(10) found that a 110° recline with lumbar support 4″ deep is ideal. Learn more in this lumbar support special:
Adjustable Headrest = Straight Neck
Paired with a 25-45° lower back curve, a 0° neck tilt is a textbook-perfect neutral posture. To achieve a 0° neck tilt, set the backrest to a 100° angle and sit as straight as you can.
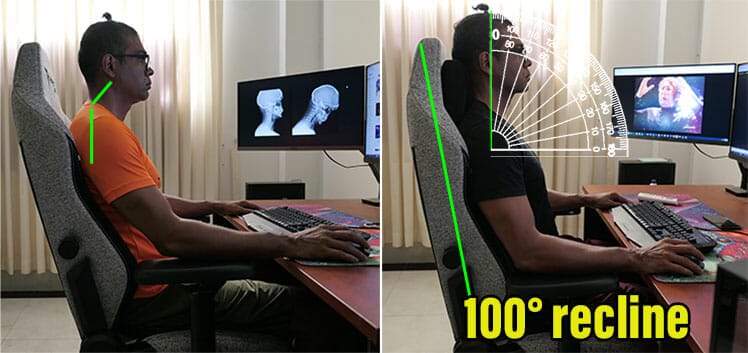
The image on the left is an advanced gaming chair posture. To achieve it, you’ll need to have already decent posture habits and strong back muscles. Luckily, since most new gaming chair users have neither, there’s a workaround.
A full-back gaming chair’s deep recline gives your body everything it needs to slowly adapt. the time it needs to adapt. For instance, if sitting straight with a sharp 100° recline feels too intense, deepen the recline to around 110-120°.

Then, gravity will help to keep your spine straight as you lean back in the chair. After a few days of sitting this way. your back muscles should get stronger. Eventually, you should be ready to try for a clean 0° neck tilt.
As proof of concept, it took me five days of practice to achieve this posture. Then, muscle memory kicked in. Now, I sit with a 0° neck as a habit. As a result, I enjoy insane comfort in my chair, plus a taller, cleaner standing posture out of my chair.
During my transition, three world-leading esports therapists shared insights on the transition. In brief, you’ll need strong back muscles and discipline. Your reward: near-perfect sitting — and standing — posture. Learn more:
Adjustable Armrests = Spinal Relief
Peter Opsvik is a well-known Norwegian industrial designer. In his book Rethinking Sitting, he notes that when seated, “… our arms require both freedom to move and lots of opportunities for support.”

Moveable chair armrests adjust to your workstation to ease the load on the back. A 170-pound man’s spinal column carries arms weighing around ten pounds each. Without effective arm bracing, the neck, shoulder, and back muscles do the work.
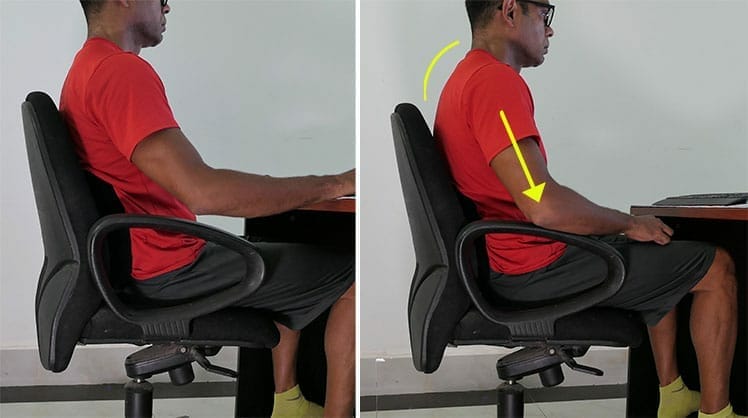

As the muscles tire, the weight of the arms forces the head to tilt forward. In a neutral position, an adult head places a 10-12 pound load on the spine(11).
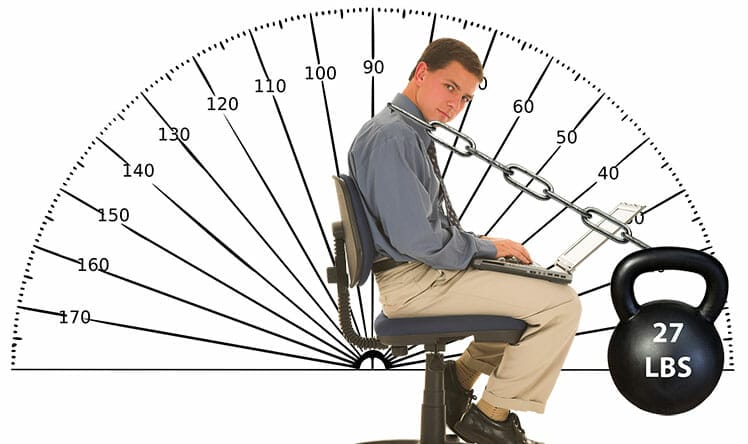
As the head tilts forward by 15 degrees, the spinal load increases to 27 pounds. At a 30-degree forward tilt, the load increases to 40 pounds.
How do gaming chair armrests help?
Many cheap gaming chairs have ‘1D’ armrests. That means they adjust in one way: vertically (up or down). Basic 1D armrests are usually enough to align with a work surface.

Then, instead of your spine supporting arm weight, the chair does the work. As well, aligning armrests to a work surface reduces wrist strain and the threat of carpal tunnel syndrome. When the wrist gets overworked, pressure hits the median nerve. That causes chronic pain and swelling.

Arm support reduces strain on the shoulders and wrists while users sit in neutral postures. That enables long bouts of sitting without harmful side effects.
Reclining Backrest = Seated Movement
Gaming chairs come stacked with features that support good posture. Even so, that doesn’t change the fact that the human body isn’t designed to sit in a chair.
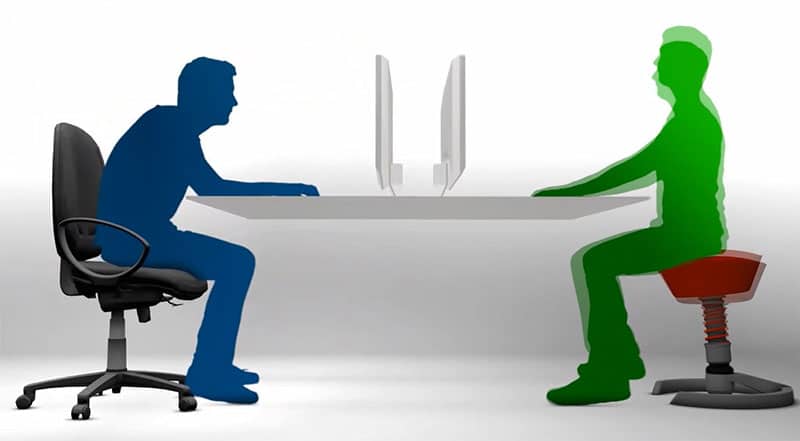

Thus, most ergonomic scientists suggest neutral postures combined with regular position changes. Active sitting is also known as ‘dynamic sitting’.
The point is to engage back, leg, and abdominal muscles while seated. Small position changes keep relevant muscle groups active. A gaming chair’s reclining backrest makes this easy.

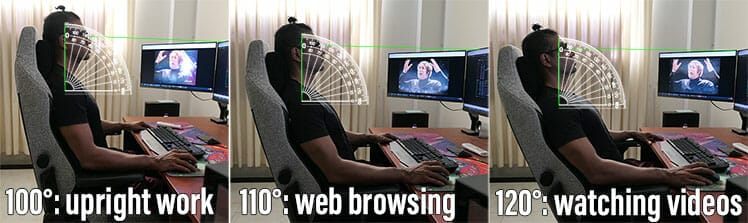
For upright desk work, setting a recline between 100-120 degrees works well. To add movement, simply toggle your recline every so often by a few degrees.
Note that the best feature to ensure seated movement is your own two legs. Walking around every 20 minutes or so will activate muscles, boost blood flow and rest your brain much better than a reclining backrest!
Seat Styles: Flat Vs Bladed
Some gaming chairs have flat seats while others have bladed ones. The latter type serves an ergonomic purpose: ridged edges dissuade users from putting their feet up. Since neutral postures rely on having planted feet, this helps to promote good posture.
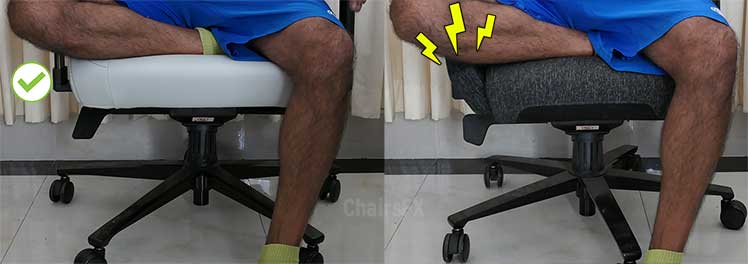
On the flip side, gaming chairs with flat seats give you more freedom. You can sit with planted feet, put one up, or even sit cross-legged. Having the freedom to sit as you like is insanely comfortable.

The problem goes back to muscular adaptation. If you sit too often in certain positions, muscles and fascia will adapt. Over time, that can break down good posture habits and ruin your spine!

The bottom line is that there’s no perfect sitting style for both comfort and health. Locking yourself in perfect posture all the time can feel stifling. On the flipside, sitting too often in casual positions can ruin good posture habits.
The best option seems to be somewhere in between the two extremes:
Gaming Chair Back Support Realities
A gaming chair is not a magic solution to cure back pain. Rather, it’s a tool that — with proper usage — can help to improve your health, happiness, and productivity.
The Perfect Sitting Posture Doesn’t Exist
A perfect neutral sitting posture includes a 25-45° lower back curve and a 0° neck tilt. But since sitting rigidly is counterproductive, imperfect dynamic neutral variations are preferable. This has created confusion among physiotherapists.
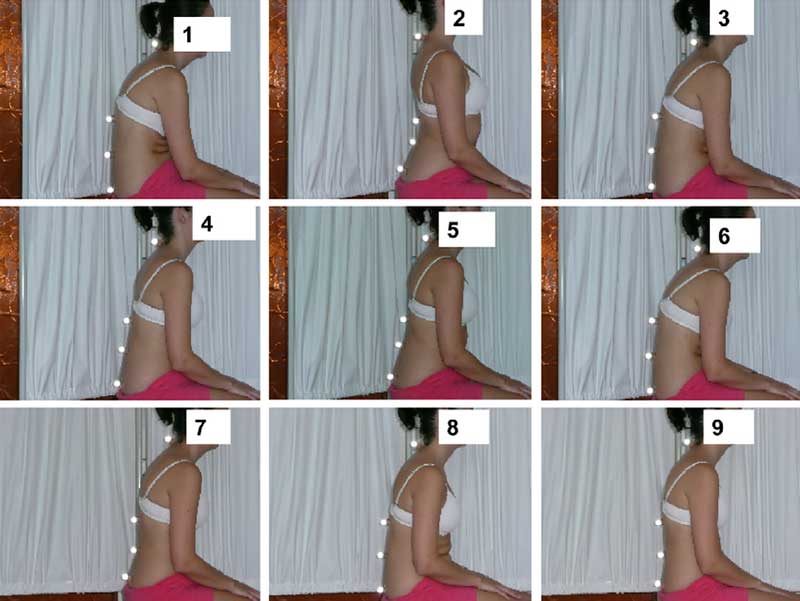
A recent study asked 295 European physiotherapists to choose the best neutral sitting posture from nine options. 85% chose either posture 5 (30.5%) or posture 9 (54.9%).
This shows that there’s no clear consensus on what constitutes a healthy seated neutral spine posture. As a result, physiotherapists give postural advice using their own subjective ideas of what defines ‘good posture’.
Gaming Chair + Fitness Yields Best Results
Many of the world’s top esports teams use racing-style gaming chairs. However, few teach their players to maintain good posture while they sit.

Instead, they employ nutritionists, mental coaches, and physical therapists to optimize their players’ lifestyle habits. The belief is that healthy, rested players perform better.

ChairsFX spoke to some esports doctors about the health benefits of gaming chairs. Dr. Jordan Tsai works with Cloud9, TSM, Evil Geniuses, 100 Thieves, and other top teams. He’s also on Secretlab’s Ergonomics Advisory Board.
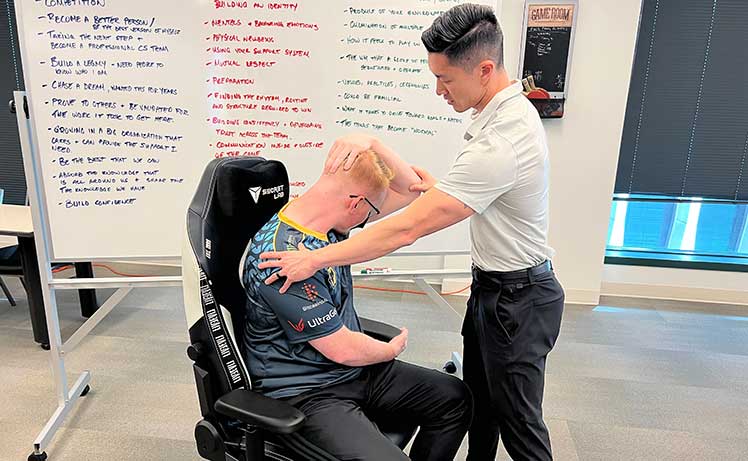
In his opinion, a good chair is the least important factor for healthy deskwork. Instead, “A regular range of motion exercises, strengthening, and stretching are all critical.”
Dr. William Duncan works with both esports pros and traditional athletes. He concurs. “Postural issues typically arise from poor strength and endurance in the postural muscles — not the type of chair.
If you work on strength & endurance and use a good chair, this will most likely resolve the source of your symptoms and allow you to play longer.”
Improper Use Can Ruin Your Experience
Sitting with planted feet, a supported lumbar curve, and a mild recline is the best way to sit in a gaming chair. After a few adjustment days, sitting this way should feel insanely comfortable. If it doesn’t, one of three aspects may be off:
- Wrong chair size: if your chair is too small or large for your body, neutral postures will distort.
- Improper usage: sitting with a spine like a banana peel negates ergonomic benefits.
- Sloppy lifestyle: poor nutrition or sleep will leave you ill-prepared to try sitting straight.
Conclusion
Gaming chairs are good for your back the way all ergonomic chairs are. Regardless of the model, adjustable lumbar + arms and a reclining backrest provide support for neutral sitting positions.

Beyond the chair, frequent breaks, regular exercise, and healthy lifestyles while keeping you physically and mentally on-point.

Bottom line: with proper usage, gaming chairs are good for your back and neck. While sitting, focus on maintaining neutral postures. Beyond your sitting technique, add these tactics for best results:
- Frequent breaks: standing up to stretch boosts circulation and keeps muscles active.
- Regular exercise: resistance training in the gym 4 x per week.
- Healthy lifestyle: clean eating + sound sleep
With neutral sitting techniques and healthy lifestyle habits, gaming chair users can enjoy deep relaxation without any guilt — or musculoskeletal harm.
User Guide: How To Sit In A Gaming Chair
Footnotes
- Lee Herrington, ‘Assessment of the degree of pelvic tilt within a normal asymptomatic population’, Manual Therapy Volume 16, Issue 6, December 2011, Pages 646-648 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1356689X11000816, (accessed 19 Dec. 2021).
- D D Harrison, et al. ‘Sitting biomechanics part I: review of the literature’, J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 1999 Nov-Dec;22(9):594-609. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10626703/, (accessed 8 March 2022).
- Kaja Kastelic, et al. ‘Sitting and low back disorders: an overview of the most commonly suggested harmful mechanisms’. Collegium Antropologicum 42(1):73-79, March 2018. Read abstract (accessed 12 March 2022).
- ‘Musculoskeletal conditions’. WHO Fact Sheets, 8 February 2021. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/musculoskeletal-conditions (accessed 12 March 2022).
- Secretlab. February 21, 2022. Facebook. Retrieved March 12, 2022, from https://www.facebook.com/Secretlab/photos/3180512355565376
- Erin M. Friend, PT, DPT, CEAS, ‘Poor Posture And Its Effects On The Body’. National Spine Health Foundation, April 8, 2015. https://spinehealth.org/poor-posture-and-its-effects-on-the-body/, (accessed 8 March 2022).
- ‘Why am I tired all the time?’. Sleep and tiredness. https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/sleep-and-tiredness/why-am-i-tired-all-the-time/, (accessed 8 March 2022).
- Erik Peper, ‘Increase or Decrease Depression: How Body Postures Influence Your Energy Level’. Biofeedback 40(3):125-130, September 2012. DOI: 10.5298/1081-5937-40.3.01, (accessed 8 March 2022).
- Calodagh McCumskey. ‘The benefits of achieving good posture’. Wellbeing & Meditation, July 14 2018. https://www.independent.ie/regionals/braypeople/lifestyle/the-benefits-of-achieving-good-posture-37103775.html, (accessed 8 March 2022).
- Jennifer Pynt, et al. ‘Seeking the Optimal Posture of the Seated Lumbar Spine’. Physiotherapy Theory and Practice 17:5, January 2001. DOI: 10.1080/09593980151143228, (accessed 8 March 2022).
- Laura Sullivan. ‘Keep Your Head Up: ‘Text Neck’ Takes A Toll On The Spine’. The Two-Way, November 20, 2014. https://www.npr.org/sections/thetwo-way/2014/11/20/365473750/keep-your-head-up-text-neck-can-take-a-toll-on-the-spine, (accessed 8 March 2022).




