The origins of science-backed ergonomics dates back to NASA research from 1973. In 1994, the Handbook of Human Factors and Ergonomics summarized NASA’s findings for office furniture developers. Since then, most institutional ergonomic guidelines have reached the same physiological conclusions. This data gives us a clear, sensible ergonomic seating definition for 2024 desk workers.

The broadest definition of ‘ergonomic’ is ‘adjustable’. In seating terms, three adjustable features qualify a chair as ‘ergonomic’. These are: adjustable lumbar + arms + reclining backrest.

Combined, these features are meant to support neutral sitting postures. These postures look similar in any type of chair with the requisite trio of adjustable components:
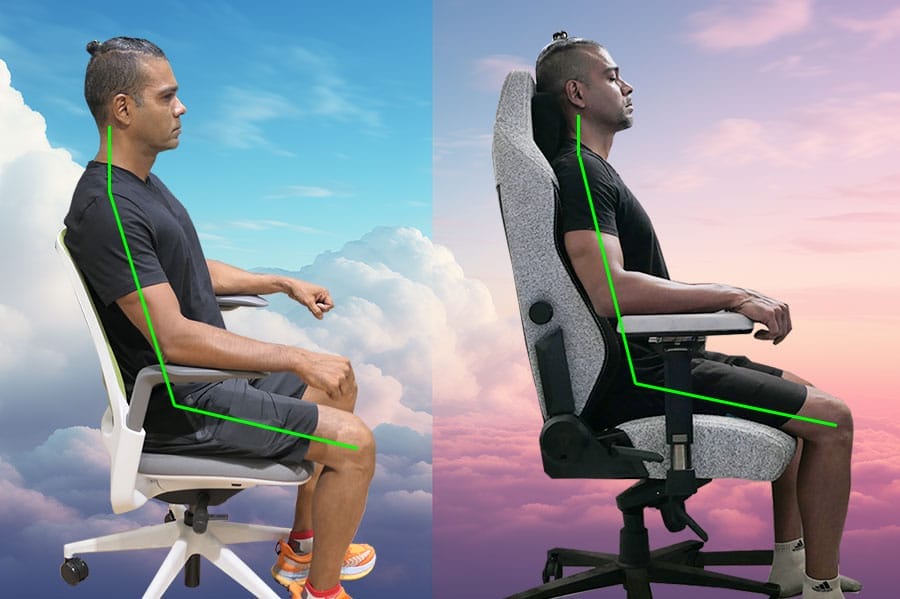

With planted feet, a supported lumbar spine, supported arms, and a customizable recline (100° is ideal), the type of ergonomic chair being used doesn’t matter.

Tuck your hips, plant your feet, and support your lower back with a backrest set to 100°. That’s the applicable gist of healthy sitting science boiled down.
51 Year Ergonomic Science Summary
The science of healthy sitting emerged from outer space in 1973. By the mid-1990s, this science was well documented for office furniture developers. Here’s a summary of the historical highlights:
Origins: Neutral Sitting Postures
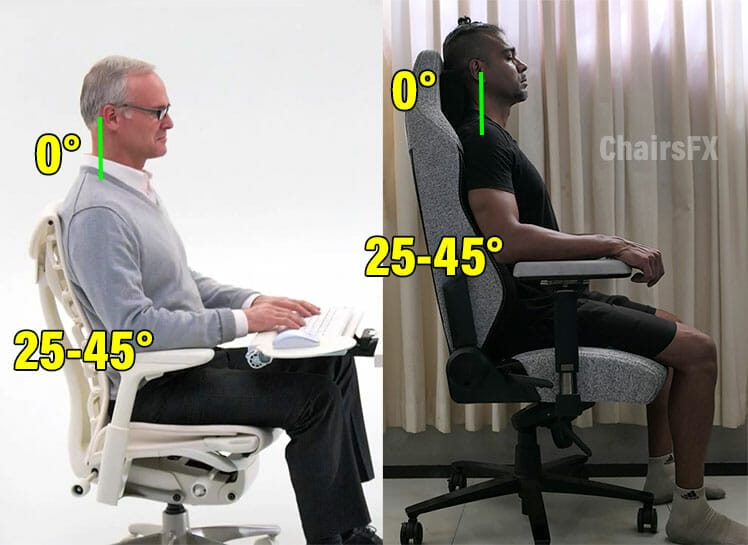
The healthiest way to sit for long periods is using neutral sitting postures. These align the spine into a healthy standing position. That includes a 0° neck tilt and 25-45° lower back curve.
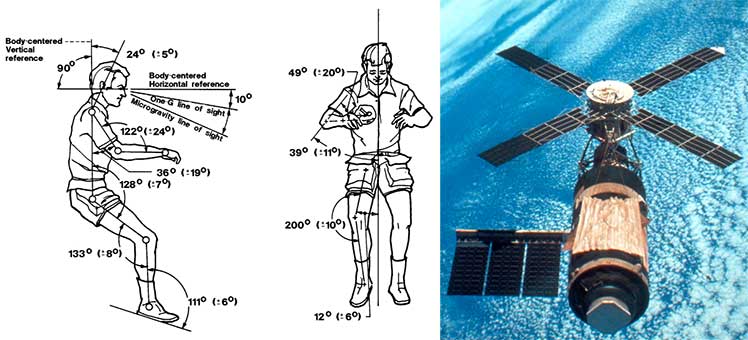
This technology landed from outer space in 1973. Then, NASA scientists observed astronauts aboard the Skylab Space Station. They noticed that when relaxed, astronauts always fell into neutral body postures (NBP).

In 1994, the Herman Miller Aeron debuted as the world’s first mainstream ergonomic chair for the computing era. By the late 1990s, a famous review of ergonomic literature(1) boiled healthy sitting mechanics down to three parts.

- The healthiest way to sit for long periods is with a neutral posture. This aligns the spine into a healthy standing posture (25-45° lower back curve and 0° neck tilt).
- To support neutral postures, an ‘ergonomic’ chair needs an adjustable lumbar, adjustable arms, and a reclining backrest.
- Fixed neutral postures strain muscles and clog circulation. As a result, users should strive for dynamic neutral postures with frequent movement.
Once you grasp neutral basics, they’re easy to apply yourself:
Related: Gaming Chair Neutral Quickstart | Neutral Office Chair Quickstart
Ergonomic Seating Definition
A chair qualifies as ‘ergonomic’ by having three key adjustable components. Adjustable lumbar support aligns the spine. Adjustable arms provide extra bracing to hold the spine upright. A reclining backrest lets a seated body move.

Combined, these features support the spine into a healthy standing alignment. That includes a 25-45° lower back curve and a 0° neck tilt. Then, users can sit for long periods without muscle strain.
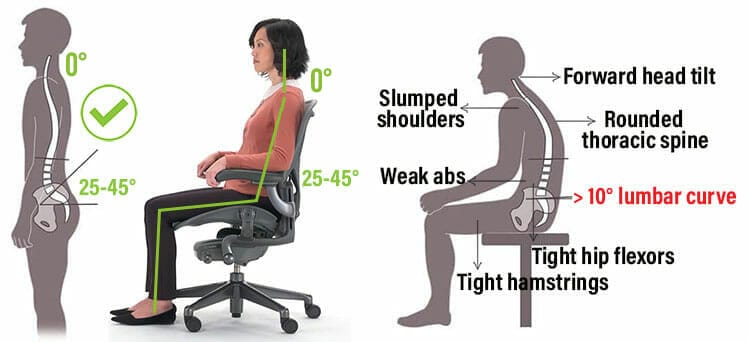
Without muscle strain, the brain gains more power. As a result, esports and desk working professionals enjoy long periods of comfortable, energized computing with razor-sharp focus.
Institutional Ergonomic Guidelines
This section summarizes ergonomic definitions from institutional ergonomic leaders. All share the same recommendations:
- Neutral postures are the healthiest while working at a desk.
- To support dynamic neutral postures, an ergonomic chair needs an adjustable lumbar, adjustable arms, and a reclining backrest.
OSHA Computing Chair Guidelines
The Occupational Safety & Health Administration documents safety standards for American workers.

Its ergonomic seating guidelines(2) rehash the need for three essential adjustable features:
- Backrest: should recline at least 15 degrees from a vertical position.
- Lumbar support: should be height-adjustable to fit the lower back.
- Armrests: should be adjustable so that the arms fall freely from the shoulders.
OSHA guidelines also advise: “adjust your chair along with appropriately placing your monitor, keyboard, and desk.”

BIFMA ergonomic guidelines
The Business and Institutional Furniture Manufacturers Association (BIFMA) was founded in 1973. It serves North American furniture manufacturers by providing furniture safety standards. Manufacturers can then test their products to determine if they meet BIFMA standards.

In 2002, the BIFMA organization first released ergonomic guidelines for office furniture. Its latest 2019 seating guidelines(3) contain these seating points:
- Height of seat: should allow the user’s feet to plant onto the floor or a footrest.
- Depth of seat: should be deep enough so that the back of the knees do not touch the front of the seat.
- Seat width: should be wide enough to accommodate the user’s hips.
- Backrest: should conform to the shape of the user’s spine. It should also have lumbar support that maintains the lordotic curvature of the lumbar spine.
- Armrests: should be adjustable up and down, plus in and out. This helps to relieve neck, shoulder, and back stress.
BIFMA also recommends that an ergonomic chair provide a healthy range of motion. The seat and backrest should allow varied postures.
Specifically, the backrest should recline from 90° to at least 115°. The only guideline for seat tilt is to ensure the torso-to-thigh angle is not less than 90°.
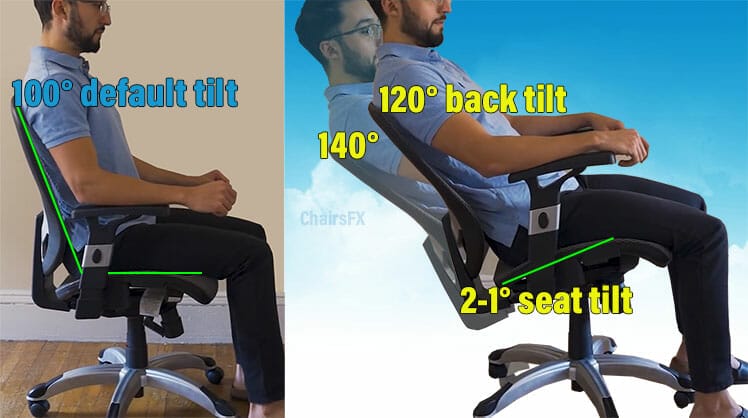
This is important to keep in mind when peddlers try to upsell people on synchro tilt. That feature tilts the seat in proportion to the backrest as the user reclines. Based on BIFMA Guidelines, it’s a luxury, not a necessity!
Human Factors and Ergonomics Handbook
The Handbook of Human Factors and Ergonomics documents the latest standards in workplace design. Its first edition came out in 2004.

The fifth edition came out with a major update in 2021. Even so, it retains most back support fundamentals of the legacy edition:
Legacy Seating Essentials
All editions of the Handbook share the same ideas about ergonomic seating:
The purpose of good seating is to provide stable body support and a dynamic posture. It should be comfortable over long periods and physiologically sound. It should also be appropriate to the task being performed.
The user’s workstation should support good posture with a few basics. First, they should be able to see the screen without moving their head. As well, the keyboard, mouse, or document they are working on should be within easy reach.

Each Handbook cites five key features that all ergonomic chairs should have:
- Chair adjustment controls should be easy to operate from a seated position.
- The chair and adjustment mechanisms should be rugged.
- Chairs should have adjustable armrests.
- The seat should be padded to ensure comfort.
- The chair should allow alterations in posture and freedom of movement.
Ergonomic Functionality Requirements
Lumbar Support
Adjustable lumbar support helps to maintain the natural curvature of the lower spine. The lumbar support should be between 6″ to 10″ above the compressed seat height, with a depth of around 1.5 inches (4 cm).
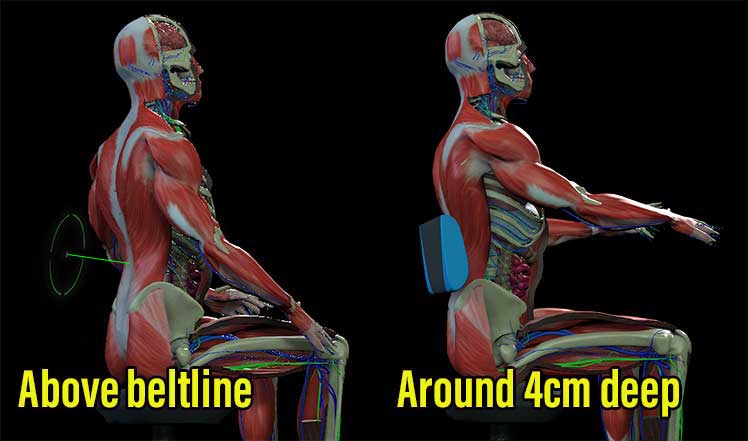
Learn more: Lumbar Support Biomechanics For Ergonomic Beginners
Seat Height & Depth
The seat’s height should be adjusted so the user can rest their feet flat on the floor. It should also place the hips slightly higher than the knees. That helps to reduce pressure on the thighs and buttocks.
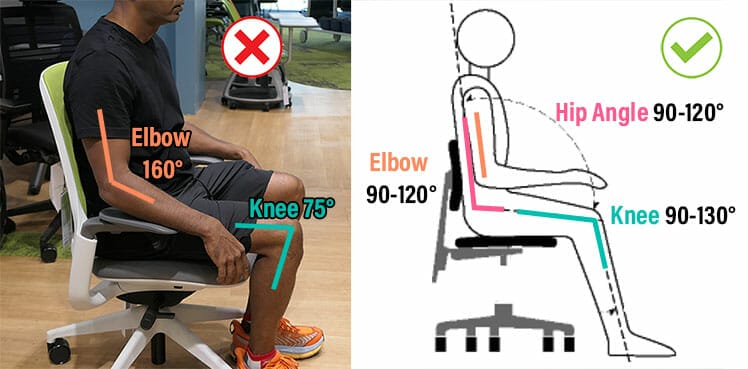
The seat’s depth should allow at least two fingers of space between the back of the knees and the seat’s lip.

A seat that’s too deep will pull the user’s knees forward, flatten their lower back curve, and round their upper spine.
Learn more: Gaming Chair Seat Sizing Guide
Backrest Angles
Reclined angles of 110° or greater reduce fatigue. Sitting with an upright 100° is good for your spine, but strenuous on the back muscles.

Armrests
Armrests at the right height support the neck and shoulders. Adjustable armrests should be height adjustable with a range of at least 4″.
Updated Ergonomic Standards
The biggest difference from the (2012) fourth edition is a shift in priorities. The previous edition focused on back support that mitigates musculoskeletal problems.

The fifth edition cites multi-device computing as a greater priority. As people immerse in near-virtual worlds, physical and mental technostress issues have arisen.
In sum, beyond good back support, a modern ergonomic workstation must also do two things. First, provide multi-device support for the back and neck while desktop or mobile computing.
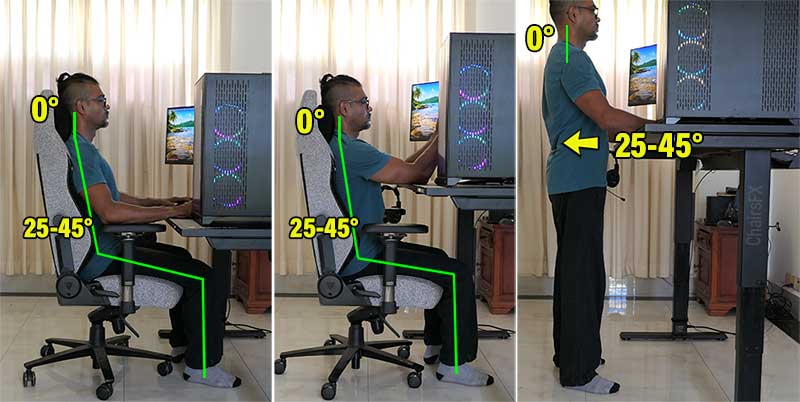

Second, provide more opportunities to move. At present, an ergonomic chair plus a sit-to-stand desk best supports these new standards:
Cornell Ergonomic Guidelines
Alan Hedge is a Professor in the Department of Design and Environmental Analysis at Cornell University. His 2013 paper on ergonomic seating(4) compiled the findings of several leading studies.

The biomechanical gist:
- Proper sitting requires a pelvic rotation that creates lumbar lordosis.
- Lumbar, thoracic, and cervical muscle activity decreases with a backrest incline to 110°.
- Lumbar disc pressure and back muscle activity are lowest with a supported recline angle of 110° – 130°.
- A high proportion of chair users make height adjustments to their lumbar support.
- After 1 hour, there is spinal shrinkage with static sitting. In contrast, the spine expands with dynamic sitting where the seat pan swivels.
Movement Is Essential
In 2015, Hedge updated his guidelines to include at least two hours of neutral standing (within a 7.5 hour workday). This amount of standing would boost movement without excessively straining the body.
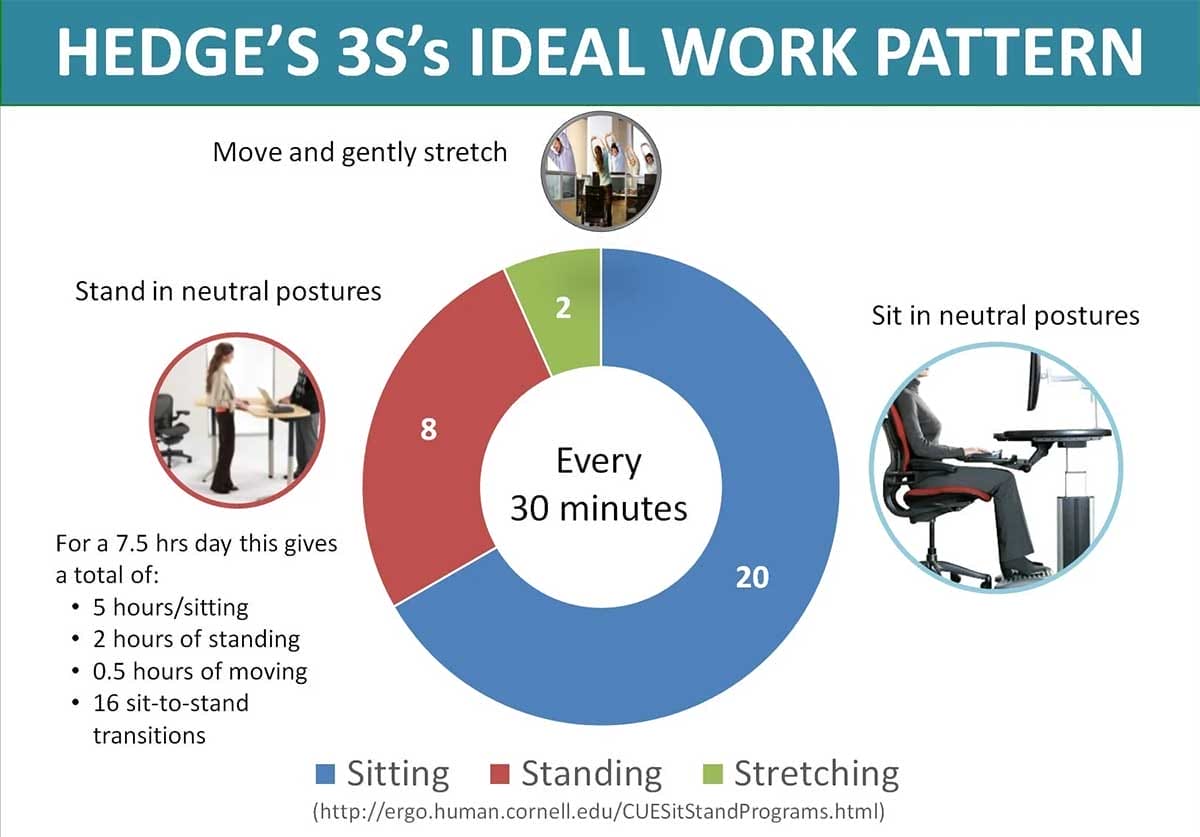
Hedge’s recommendations were published in Cornell’s Sit-Stand guidelines(5). Key points:
- Movement is healthy: a large body of research has shown that frequent microbreaks improves levels of comfort, work performance, and reduces the risks of musculoskeletal injuries.
- Standing is strenuous: standing uses ~20% more energy than sitting. It also puts greater strain on the circulatory system and on the legs and feet.
- Excessive standing equipment: provide employees with anti-fatigue footwear. Also give them chairs to allow them to sit down during rest breaks.
Hedge’s advice:
Condensed Ergonomic Guidelines
OSHA, BIFMA, Dr. Hedge, and the 5th-edition Human Factors Handbook all agree that ‘ergonomic’ means adjustable. To support dynamic neutral postures, a chair needs adjustable lumbar support, adjustable arms, and a reclining backrest. Here’s how those features apply to a full-back gaming chair:
Below is a closer look at what leading scholars advise for each adjustable part:
Lumbar Support
This is the most important component in any ergonomic chair. Mild pressure applied to the lower back reflexively triggers the upper back to straighten.
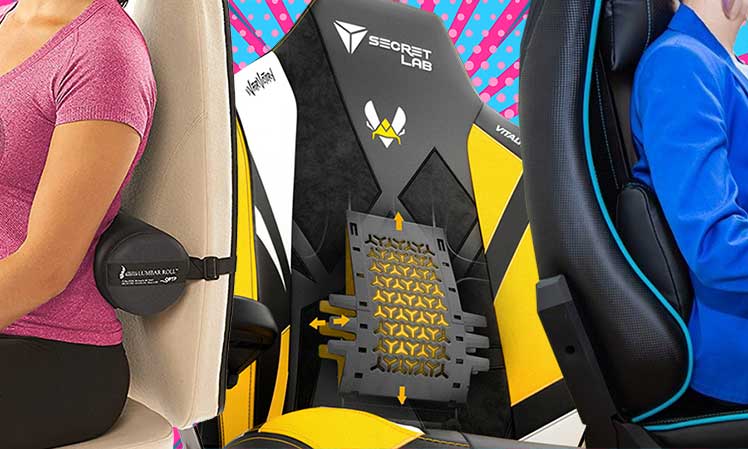

This comprehensive 2009 peer review(6) summarizes the key technical factors:
- When standing, the optimal lordotic angle is between 20-45 degrees.
- Unsupported sitting reduces lumbar lordosis by 50%. It also increases intradiscal pressure at the third lumbar vertebra by 40%.
- When sitting with a back angle of 110° and a lumbar support 4 cm deep, lumbar lordosis averages a healthy 47° angle.
- The depth of the lumbar support depends on the individual. If lumbar support causes discomfort, it means it is set too high, too low, or too deep.
- A sustained lordotic sitting position decreases disc pressure and thereby disc degeneration.
For best results, it’s important to combine these factors with physiological realities. The average adult spine is around 30″ long for men and 24″ long for women.
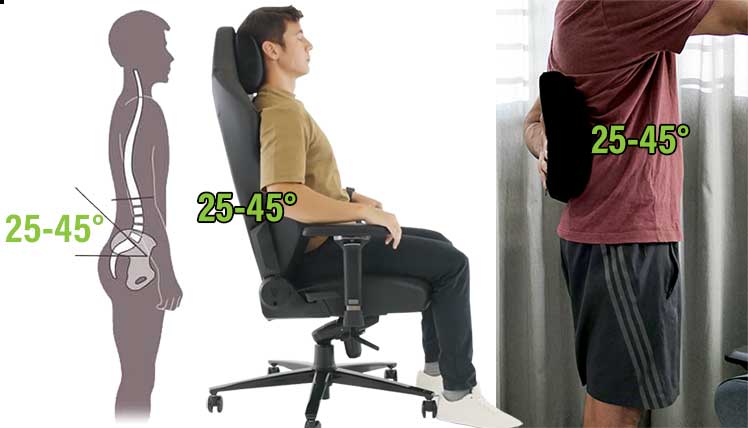

The average man should position his lumbar support around 7.5″ above the seat. An average-sized woman should aim for support set to around 5.5″ higher than the seat.
Lumbar Support Biomechanics For Healthy Sitting
Related: Best Lumbar Support Types – Good Ergonomics Vs Gimmicks
Reclining backrest
The point of an ergonomic chair is to reduce pressure on your back. With a backrest recline of 110°, lumbar, thoracic, and cervical muscle activity decreases.

With a supported recline between 110° and 130°, back muscle activity is the lowest.
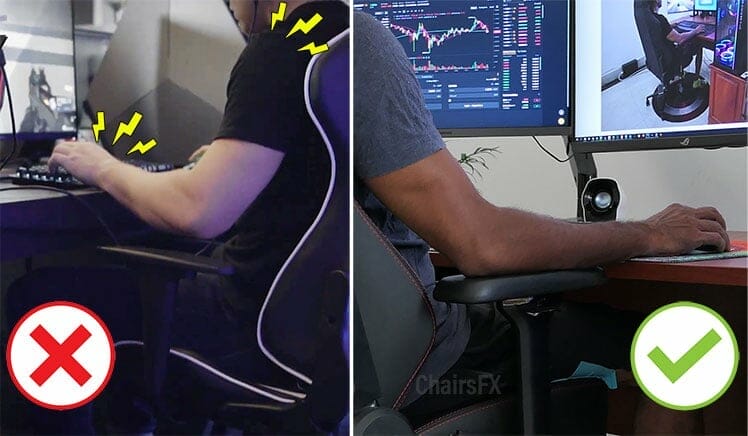
Adjustable armrests
A human arm weighs around 6% of one’s total body weight. A 170-pound person’s arms weigh around 10 pounds each. Without armrest support, your spine bears the load of holding your arms up against gravity.
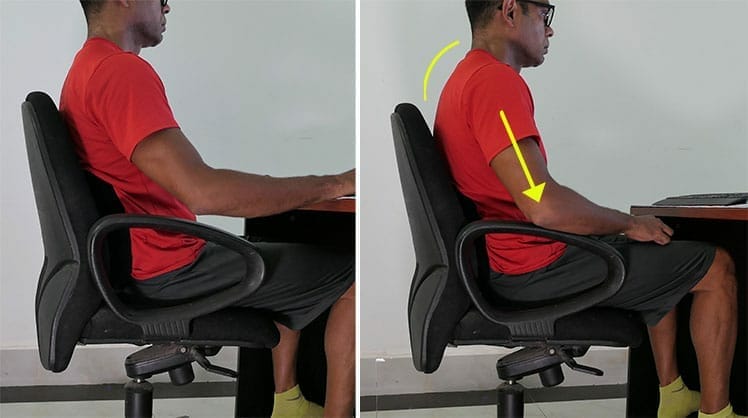

While computing, that places unnecessary strain on the spine, shoulders, and neck. As muscles tire, the weight of the arms forces the head to tilt forward.
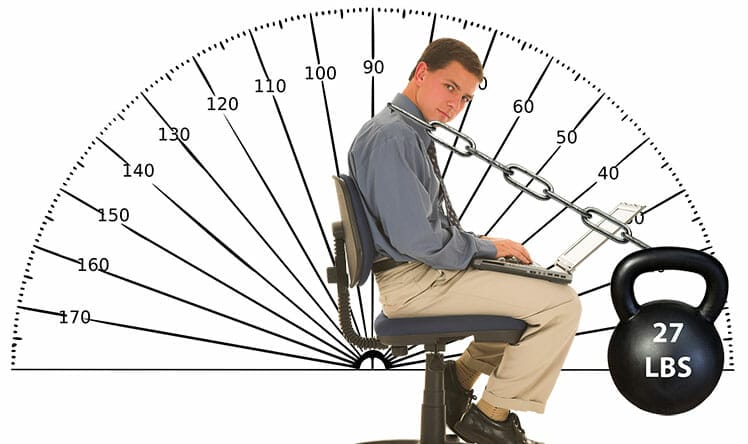
In a neutral position with a 0° neck tilt, an adult head places around a 10-pound load on the spine(7). As the head tilts forward by 15 degrees, the spinal load increases to 27 pounds.

At a 30-degree forward tilt, the load increases to 40 pounds. That’s where adjustable armrests come in. With planted feet and arms synced with a desk, sitting up straight becomes much easier.
Ergonomic Goal: Musculoskeletal Relief
Humans are not designed to sit for long periods. We know this because the lumbar spine falls out of alignment when in a sitting position. When standing, a healthy lumbar spine curves inward at a 20-45° angle. Sitting without lumbar support cuts that angle in half(8).
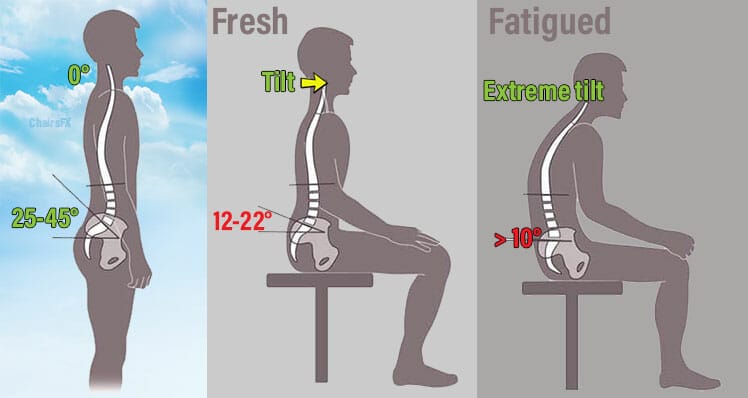
Then, back muscles must work harder to hold the spine upright. Once muscles tire, the upper back bends. That flattens the lumbar curve to less than 10°. Long periods in that position shortens hips flexors, pulling the whole body out of alignment.
The lower back tightens, while core stomach muscles get longer and weaker. At the same time, quad muscles tighten the front of the leg, while hamstrings elongate and weaken from the rear.
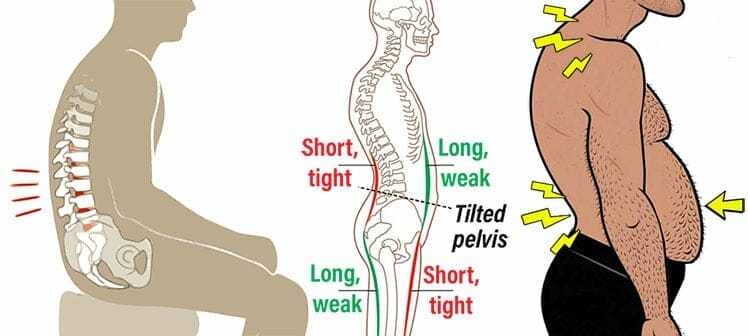
Misaligned bodies caused by poor sitting habits are endemic. In America, some studies estimate that 80% of adults suffer from anterior pelvic tilt(9). In that state, misaligned muscle pairs work against each other. That twists the pelvis from a neutral position to a tilted one.
Common Musculoskeletal Disorders
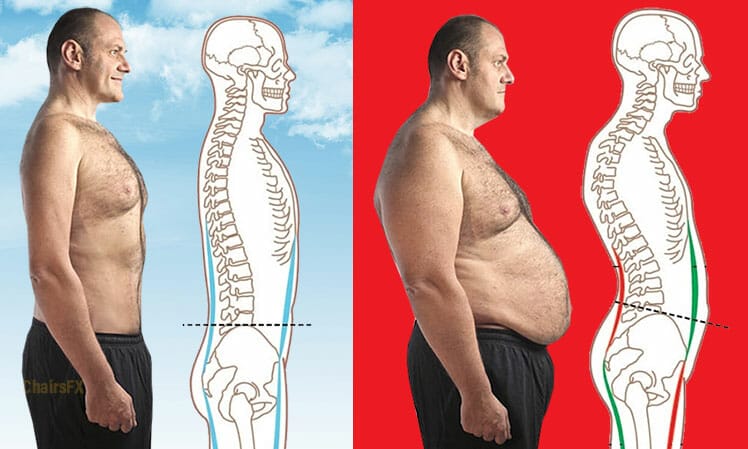
A tilted posture places excess stress on tall body parts. As that builds up, myriad musculoskeletal disorders emerge. These include:
- Low back disorders: the leading cause of disability in 160 countries.
- Chronic fatigue: misalignments overwork muscles, leaving users perpetually exhausted.
- Migraines: forward head posture strains neck muscles until pain arises.
- Wrist pain: 4 million Americans suffer from carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Neck pain: the fourth-leading cause of disability in America.
Long-term, MSDs can lead to serious chronic health problems.
Examples:
- Obesity: waist circumference increases by 3.1 cm with a 10% increase in sedentary time. As they gain weight, patients feel less compelled to move.
- Diabetes: excess sedentary time increases type 2 diabetes risks. Regular exercise only slightly offsets this risk. Symptoms include tingling extremities, dry skin, and excessive urination.
- Cancer: prolonged sitting increases colorectal, endometrial, ovarian, and prostate cancer risks. It also increases cancer mortality (mainly in women).
- Hypertension: sedentary behaviors reduce blood pressure. That alters cardiac output and total peripheral vascular resistance.
- Osteoporosis: slothful living lowers bone mineral density in the femur and hip sub-regions. That makes bones brittle and easy to break.
Learn more: Common Desk Worker Musculoskeletal Disorders In 2022
4 Pillars of Esports Performance (NEW)
Professional esports is one of the most intense, demanding desk jobs. Many first-person shooters demand up to 400 actions per minute. To succeed, players need elite speed, precision, hand-eye-coordination — and endurance.

Reducing musculoskeletal stress helps esports players perform better. This is why most pro esports teams have their players compete using ergonomic chairs. However, seating plays a very small role in the esports performance optimization equation.
For instance, Dr. Jordan Tsai once managed the Physical Therapy program for Evil Geniuses. He advised ChairsFX that a good chair is the least important part of a healthy setup!
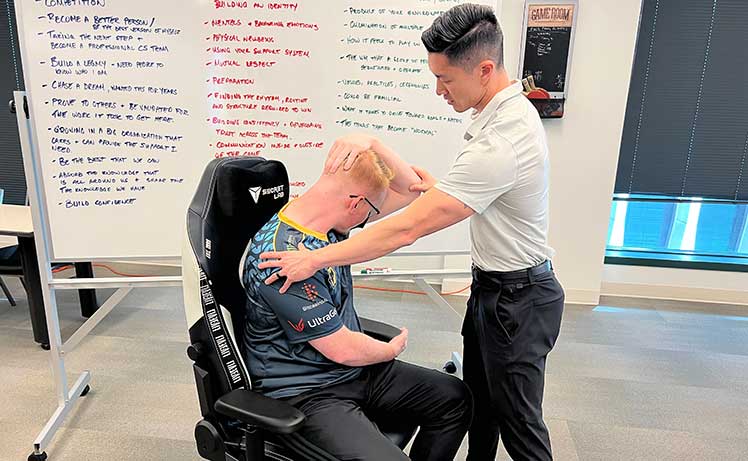
His view is consistent with the 5th edition Human Factors Handbook: movement and fitness take precedence. Good back support remains relevant as a secondary priority. “Rest/nutrition/exercises > breaks > good posture > good chair.”

This formula has since been broken down into what’s broadly called the ‘4 performance pillars’. Without a healthy 4 pillars foundation, the impact of a good ergonomic chair might be minimal.
Here are the priorities for healthy deskwork (in order of Dr. Tsai’s listed importance):
- Performance pillars: regular exercise, good nutrition, mental balance, sound sleep.
- Good posture: try to sit straight in whichever type of chair you use.
- Frequent breaks: walking breaks reset the brain, boosts blood flow, and activates sedentary muscles.
- Good ergonomic chair: choose whichever type aligns with your preferences.
Gaming Vs Ergonomic Office Chairs
Gaming chairs emerged in 2006 as niche items. Against a multi-billion-dollar ergonomic office furniture industry, they thrived. Many office chair industry players have tried to stem that tide.

“Gaming chairs are not ergonomic” is a common defense. But according to OSHA, BIFMA, and the Human Factors Handbook, this is misinformation.
In fact, any chair with adjustable arms, an adjustable lumbar, and a reclining backrest qualifies as ergonomic. These features on any type of chair are meant to support healthy neutral sitting postures.
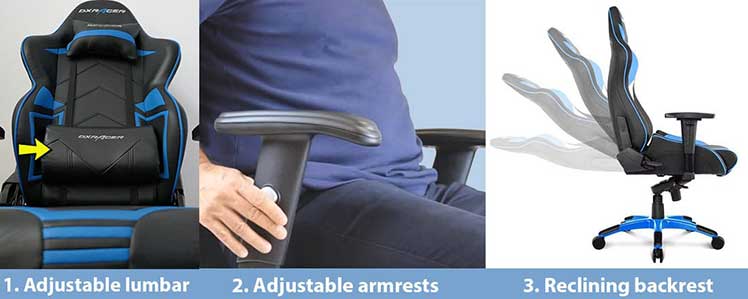
Both full-back gaming and mid-back ergo office chairs use the same support techniques. Adjustable lumbar support, armrests, and a reclining backrest give users the tools they need to sit straight – with movement.
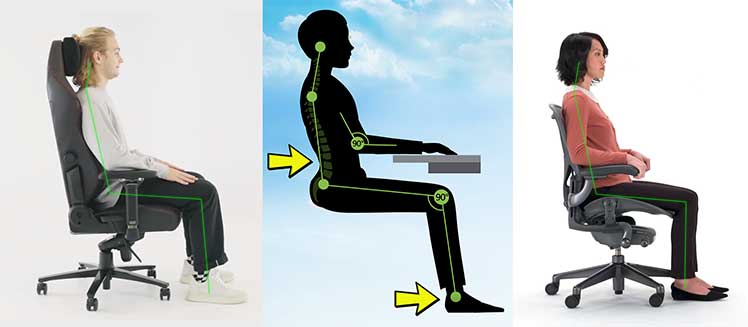
The biggest difference between the two styles is the backrest. Ergonomic office chairs come with mid-back support; gaming chairs are full-back. Mid-back chairs provide more accurate sitting support; full-back styles provide better WFH versatility.
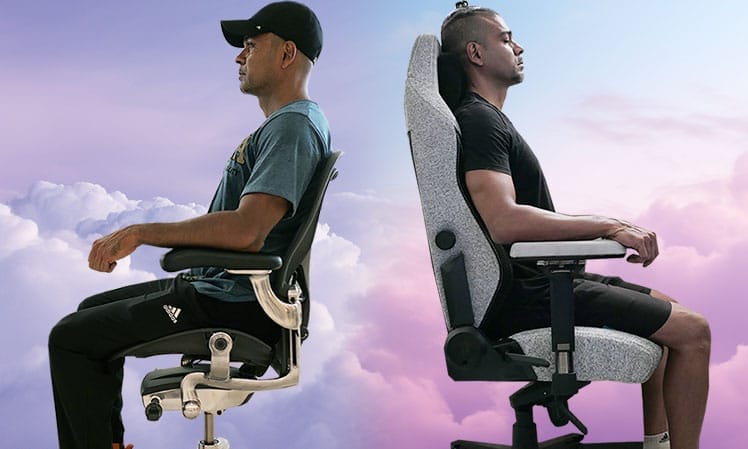

In fact, my Aeron office chair vs Titan Evo gaming chair comparison found that both chairs support near-perfect neutral postures. The biggest differences between the two were luxuries extras — these affect the psyche more than the spine!
Conclusion: Ergonomic = Adjustable
‘Ergonomic’ simply means ‘adjustable’. We can see the effect of adjustable lumbar + adjustable arms + a reclining backrest in various seating styles:

The above picture tells the story. Any chair qualifies as ‘ergonomic’ by having three adjustable features:
- Adjustable lumbar support: maintains a healthy lower back curve.
- Adjustable armrests: these support elbows and forearms while positioning hands close to the mouse and keyboard.
- Reclining backrest: a recline range of 90° to 130° (with lumbar support) reduces spinal pressure.
From a back support perspective, gaming chairs and office chairs with the necessary components do the same thing. So how to decide on one type or the other?
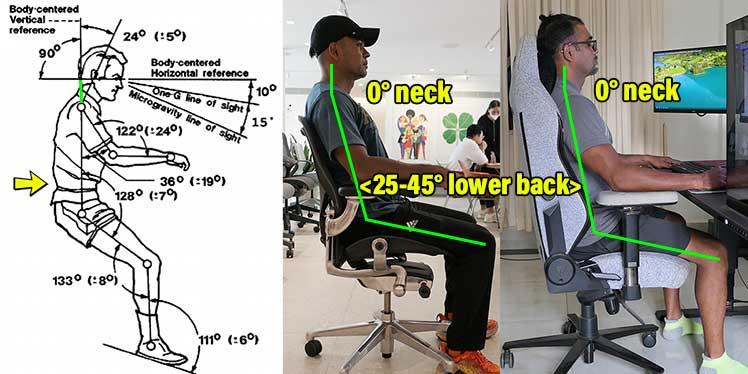

In other words, subjective psychological preferences are a major comfort factor. So are user-powered habits. With proper usage, whichever type of fully-ergonomic chair appeals to you has potential to be ‘the best’. Learn more:
Seated Comfort Factors: Physical Vs Psychological Vs Usage
Footnotes
- D D Harrison, et al. ‘Sitting biomechanics part I: review of the literature’, J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 1999 Nov-Dec;22(9):594-609. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10626703/, (accessed 8 March 2022).
- OSHA. ‘Computer Workstation Components: Chairs’. https://www.osha.gov/etools/computer-workstations/components/chairs, (accessed 8 March 2022).
- ‘BIFMA Standards Descriptions’, September 2019. https://www.bifma.org/page/StandardsShortDesc, (accessed 8 March 2022).
- Professor Alan Hedge. ‘Ergonomic Seating?’ Cornell University, August 2013. http://ergo.human.cornell.edu/studentdownloads/DEA3250pdfs/ErgoChair.pdf, (accessed 8 March 2022).
- CU Ergo. ‘Sitting and Standing at Work’. Cornell University Ergonomics Web. http://ergo.human.cornell.edu/CUESitStand.html, (accessed 8 March 2022).
- Jennifer Pynt, Martin G Mackey, ‘Seeking the Optimal Posture of the Seated Lumbar Spine’. Physiotherapy Theory and Practice 17:5, 2001, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224029048_Seeking_the_Optimal_Posture_of_the_Seated_Lumbar_Spine, (accessed 9 Jan. 2022).
- Laura Sullivan. ‘Keep Your Head Up: ‘Text Neck’ Takes A Toll On The Spine’. The Two-Way, November 20, 2014. https://www.npr.org/sections/thetwo-way/2014/11/20/365473750/keep-your-head-up-text-neck-can-take-a-toll-on-the-spine, (accessed 8 March 2022).
- Kaja Kastelic, et al. ‘Sitting and low back disorders: an overview of the most commonly suggested harmful mechanisms’. Collegium Antropologicum 42(1):73-79, March 2018. Read the abstract (accessed 20 Feb. 2022).
- Lee Herrington. ‘Assessment of the degree of pelvic tilt within a normal asymptomatic population’. Manual Therapy Volume 16, Issue 6, December 2011, Pages 646-648. doi.org/10.1016/j.math.2011.04.006 (accessed 20 Feb. 2022).




