No products in the cart.
Friday, October 18, 2024
Most Comfortable Chair? Physical Vs Psychological Factors
When you buy something using an affiliate link in this post, ChairsFX may receive a small commission, at no additional expense to you. This has no influence on our editorial content. See our Affiliate Disclosure for details.
Reading Time: 13 mins read
How to determine the comfort potential of a desk chair? The broadest definition of ‘comfort’ is ‘an absence of discomfort’. In the seating world, comfort has physical and psychological factors. Good back support promotes physical comfort. Flashy extras like colorful skins or fancy tilting features appeal to the psyche. This article breaks down physiological vs psychological seating comfort factors. You can use these to make a rational decision when buying your next chair.
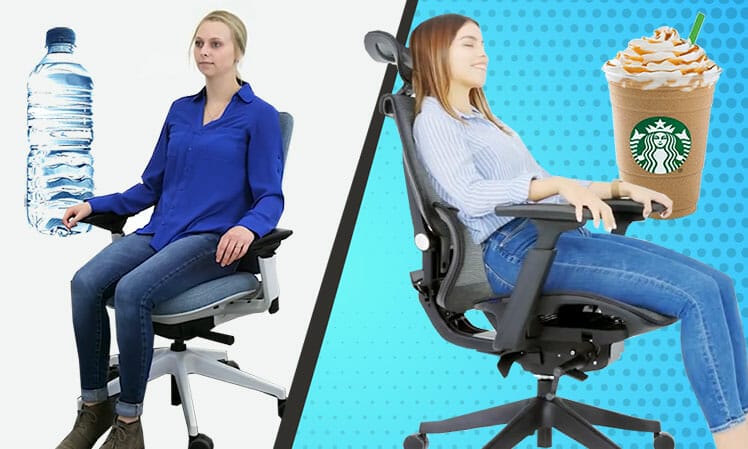

There’s no universal comfort rating system for ergonomic chairs. Even so, by approaching the question rationally, clear answers emerge. Many researchers study comfort as ‘an absence of discomfort’(1).
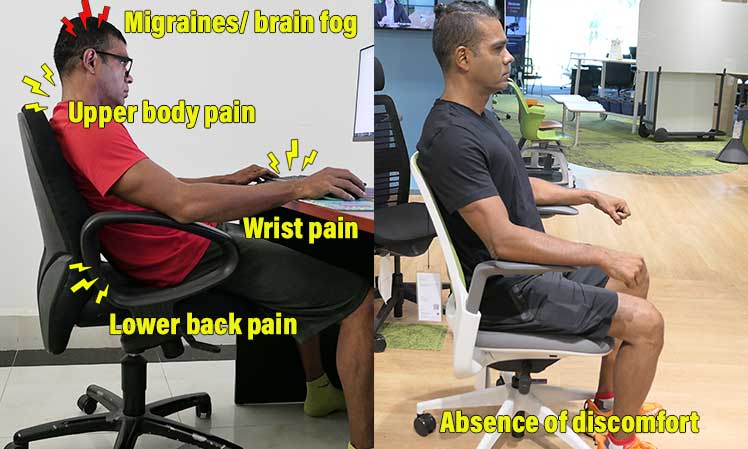
They test this by measuring physiological reactions to environmental stimuli. These can be objective (muscle activity measurements) or subjective (reported feelings).
Meanwhile, many modern car seat comfort studies consider both physiological (objective) and psychological (subjective) factors when measuring comfort potential(2).

We can also apply physical and psychological comfort aspects to desk chairs. For example, kneeling chairs are designed to support perfect posture — but only with proper form. Users must buy into the concept of engaging their back muscles to hold their torso upright.
Those who put in the effort will align their spine, lower muscle activity, and eliminate physical discomfort. However, kneeling stools look dreary.

Those who lack the motivation to maintain good form will slouch their spines instead. That will tighten their lower back, leading to ‘discomfort’. This is one example of how the perception of comfort can influence how the body responds.
Physiological Chair Comfort Factors
The ultimate point of any type of ergonomic chair is to support neutral sitting postures. Below, I’m using a Herman Miller Aeron office chair and a Secretlab Titan gaming chair to support similarly active neutral postures.
Physically, both chairs do the exact same job! The difference is that each stacks different luxuries on top of that foundation.
This section focuses on ergonomic chair aspects that promote physical comfort. Assess these qualities of a chair first. After that, you can get into perusal of psychological luxury extras.
Ergonomic Chairs Support Neutral Postures
Every ergonomic chair has the same objective: support of neutral sitting postures. All do so using the same three adjustable components.

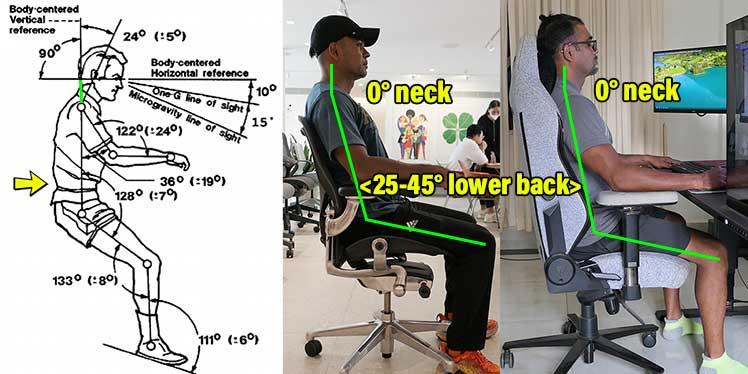
This concept first emerged in 1973. Then, NASA researchers observed astronauts in zero gravity. They noticed that astronauts often fell into active neutral body postures (NBP) while working.
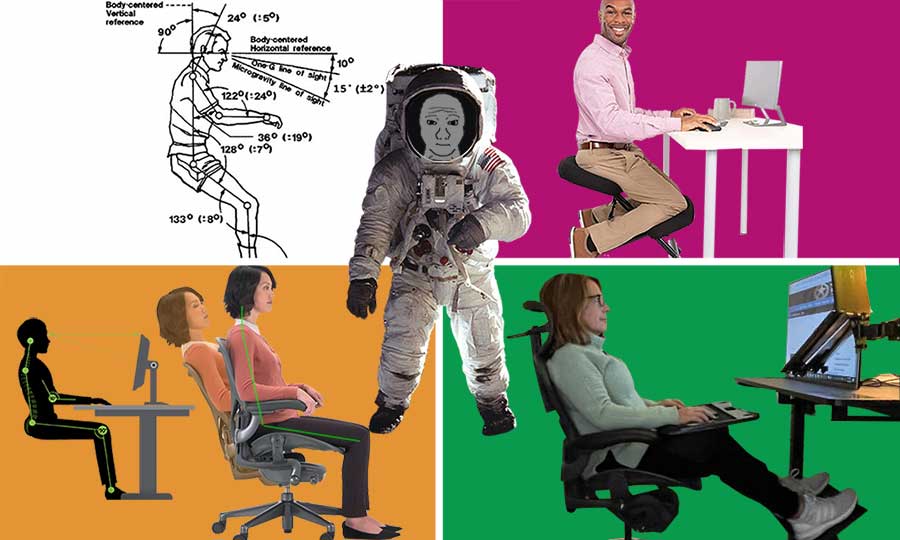

Further studies found that neutral postures work back muscles optimally, without strain. In zero gravity, that helps astronauts work comfortably for longer periods.
When NASA shared its findings, the car seat industry was one of the first to implement NBP concepts for consumers. In 2005, Nissan adopted NBP principles to produce ergonomic car seats.
Nissan’s groundbreaking Altima car seat popularized the concept of passive neutral postures among mainstream consumers.
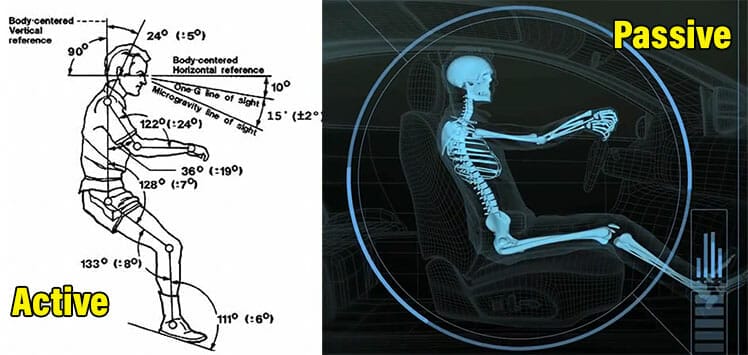
Active Vs Passive Neutral Postures
Today, the active vs passive difference remains a core concept that all ergonomic chair users should grasp:
| Type | Definition | Specs | Downside |
| Active Neutral | Engages back muscles to hold the torso up against gravity | 0° neck, 25-45° lower back curve | Demands discipline, good technique and strong, resilient back muscles |
| Passive Neutral | Lets users rest their body weight against the backrest; the chair does all the work | 0° neck, 25-45° lower back curve | Overuse can weaken back muscles and distort upper body posture |
Proper Chair Sizing
The point of an ergonomic chair is to align the spine into a neutral position. For that to happen, it’s crucial to use a chair that fits! For instance, using a seat that’s too deep for your legs will pull your knees forward.

Knees pulled forward flattens the lower back curve. That will degrade good posture rather than supporting it! Over time, that’s likely to result in lower back pain or worse.
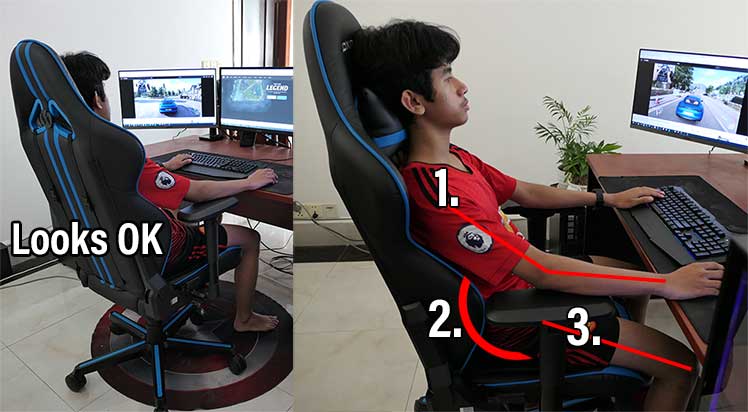

Beyond a seat too deep, a backrest too tall or a seat set too high can also cause problems. For this reason, ChairFX advises all users 5’8″ or shorter to use an ergonomic footrest.

Even if your chair costs $3000, it can still cause discomfort if the sizing is off. For the best ergonomic results, it’s crucial to choose a chair suitable for your size!
Lumbar Support Type & Fit
Lumbar support can help or hinder your sitting experience. Support set too low will curl your hips forward. Setting support too high will curve the upper spine, promoting a forward slouch.

This comprehensive peer review advises using a 110-130° recline angle with a depth of 4cm. But at what height?
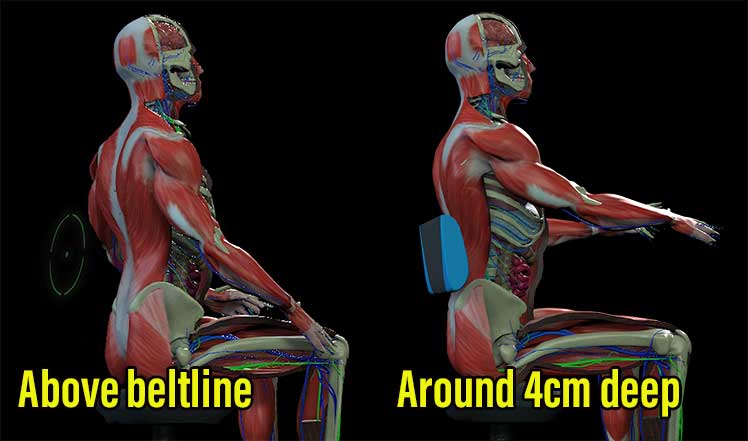
In general, your support should hit slightly above the beltline. That’s around 7.5″ above the seat for the average man/ and 5.5″ for women. There are several types to choose from.

Here are my top 4 favorite lumbar support types:
- 4-way integrated: built-in height x depth adjustability; tricky to get right.
- Height-adjustable integrated: built-in height adjustability; not as precise as 4-way systems.
- External memory foam pillow: soft and malleable; needs constant readjustment.
- Gaming chair pillow: works well; tricky to figure out for beginners.
Each of the four does a decent job. Learn more:
Psychological Comfort Factors
The previous section explained how ergonomic chairs promote both active and passive neutral postures. Revisiting the Aeron vs Titan comparison, we can see that both promote healthy neutral sitting postures.

Beyond each chair’s physical support properties are psychological extras. These do not impact the back support qualities of a chair. Rather, they add to its perceived appeal.
For instance, the Aeron comes upholstered in sleek, sexy mesh with fancy seat tilting functions. The Titan comes in a wild array of styles with full-back support and comfortable padded seats.

Here are other psychological chair attractions that take a chair’s appeal beyond good back support:
- Deep recline appeal: upright postures are healthier. Even so, many prefer slouchier reclined ones.
- Psychological headrest appeal: office chair headrests create an illusion of comfort while distorting neck posture. Yet, many love them!
- Upholstery preferences: many prefer breathable mesh or soft fabric chair covers.
- Firm vs squishy padding: firm padding provides more consistent, stable support. Softer padding feels more luxurious in the moment.
- Color psychology: different colors emit different light energies in a room. However, these effects are temporary.
- Office chair addictions:: some get so obsessed with luxury features they lose sight of the physical comfort goal!
Posture-Distorting Reclines Are Appealing
The Herman Miller Aeron’s tiny 93-104° recline range keeps users sitting upright at all times. This is great for physical comfort — but not as psychologically appealing.

For instance, a study was done on aircraft passenger seats with and without headrests. It found that when in seats without headrests, users would instinctively keep their heads balanced with a clean 0° tilt.
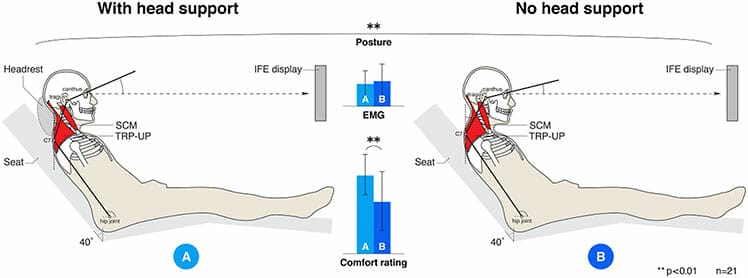
Adding a headrest did not significantly reduce the neck muscle activity of test subjects. Instead, it compelled them to tilt their heads off-center. But a tilted neck degrades postural accuracy by rounding the upper back.

Despite the loss of postural accuracy, most test subjects preferred seats with headrests, especially for passive tasks like watching in-flight films.
This explains the appeal of flashy office chairs over plain ones. For instance, the Steelcase Series 1 ($498.00) delivers superb back support. But it looks boring.

In contrast, the Flexispot C7 ($369) spices things up with full mesh upholstery, a headrest, and more flashy moving parts. Head-to-head, the Series 1 provides better physical comfort. But its psychological appeal points don’t compare with the C7 chair’s. Which would you prefer?
Relaxing Ergonomic Chairs Are Trending
Sacrificing good posture for slouchier, more casual sitting styles is trending. Last year, Haworth and Herman Miller both released pricey gaming chairs that sacrifice perfect neutral postures for more relaxed variations.

According to Herman Miller’s Gaming Jon Campbell, this caters to a generational difference in perceived comfort:
Gamers require versatility. A strong active posture is critical for gameplay, but having an equally supported, reclined position for moments of relaxation is key.Jon Campbell
Full-Back Gaming Vs Mid-Back Ergonomic Office Chairs
Gaming chairs have deep reclines and headrests. These are designed to support neutral postures while upright plus semi-neutral reclined positions. In contrast, mid-back office chairs have limited recline ranges.

These force users to sit basically upright at all times. That’s why they’re often called ‘task’ chairs: they’re strictly for doing deskwork tasks.

Versatile full-back gaming chairs deliver more versatile work-from-home support. Beyond deskwork, they support deep relaxation for other endeavors.
Bottom line: full-back chairs provide more versatile all-day sitting support. Mid-back chairs enforce stricter postures that promote focus. The former better supports casual WFH. The latter is ideal for shorter bursts of high-tensity ultra-productivity. Learn more:
Many Prefer Posture-Distorting Headrests
A study on car seats with and without headrests illustrated how headrests distort spinal posture. The human spine has 33 vertebrae divided into cervical, thoracic, and lumbar sections (plus sacrum and coccyx bones).
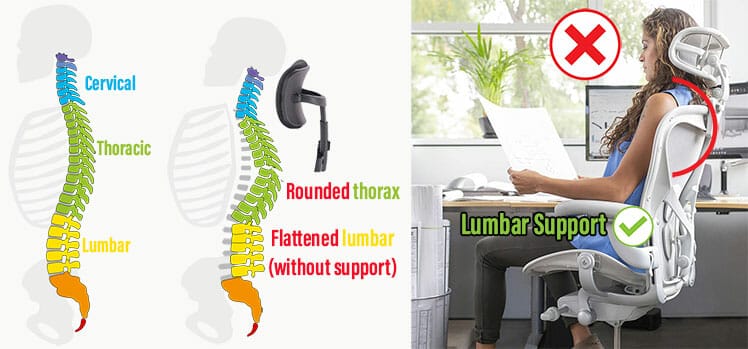
However, car seat headrests don’t support a 0° neck. Instead, using one will compel the head to tilt forward or rearward off the center line. A tilt in either direction will curve the thoracic (upper) spine outward more than normal. The same thing happens in office chairs.
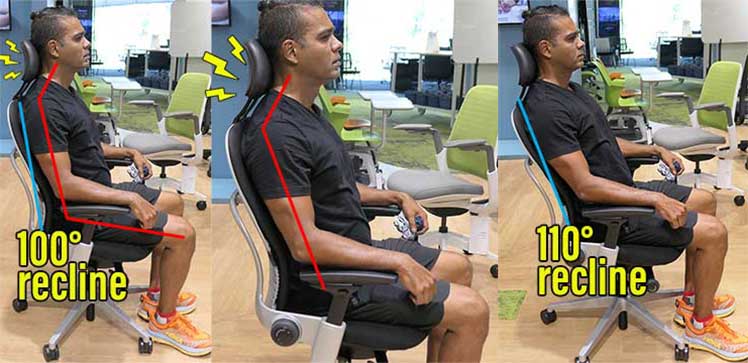
For instance, when sitting upright with a 100° recline angle, the Steelcase Leap headrest tilts my neck forward. That stresses my upper back and neck. With a more relaxed 110° recline, it’s only a bit better.

Protip: anyone suffering neck or upper back pain in an office chair should remove the headrest. Then, focus on sitting in an active neutral posture. BOOM! Problem solved. Learn more:
Upholstery Appeal
Computing chairs come in three types of upholstery: mesh; faux leather over padding, or soft fabric over padding. Which is the most comfortable? At a glance, it’s clear that mesh offers much better breathability than a fabric gaming chair.

But there are other factors to consider. At the 2020 International Comfort Conference, a comfort rating system was proposed to assess desk chair upholsteries(3).

It cites sensorial, thermophysiological (breathability), and ergonomic factors as the keys. Considering these factors, let’s compare an ultra-breathable Herman Miller Aeron against a Secretlab Mint Green SoftWeave chair. Which is more comfortable?
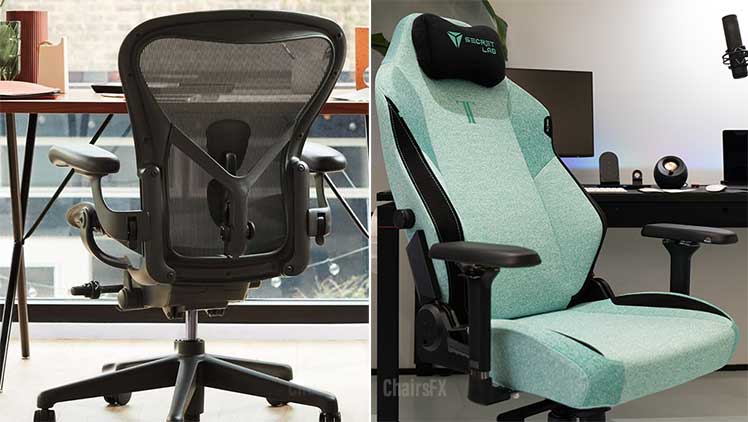

The Aeron has the thermophysiological edge by a large margin. The Titan’s soft fabric delivers more relaxing sensations than the Aeron’s synthetic, steely mesh.

Which style is better? It’s entirely subjective — wholly up to your preferences. Personally, I love the soft, soothing, homey feeling of fabric:
Firm Vs Squishy Padded Seats
One’s choice of chair padding will also impact its comfort potential. Cheaper padded chairs are squishier; more expensive ones tend to be firmer.

Softer, seat padding is more comfortable — in the short-term. Over time, it provides unstable support that overwork muscles. That’s why many people feel exhausted after long periods on a sofa.

Similar principles apply with mesh. New mesh chairs provide firm, steady support. Over time, cheaper mesh sags. Then, it starts delivering similarly unsteady support.
Case Study: Soft vs Firm Gaming Chair Padding
Related: Mesh Upholstery Pros And Cons
Color Psychology
The most vivid chair I ever tested was a bright-yellow Cyberpunk edition. For around six weeks, it seemed to light up my entire office with intense, crackling energy. Every time I entered my office was a thrill.

However, that effect only lasted for around six weeks. After that, the chair blended in as a regular part of my workspace.
But even if temporary, the color of your chair will have an impact on the energies in your workspace. Different colors produce different light energies.
Color Psychology Fundamentals
When these strike the retina, they convert to electrical impulses. Each hue sends unique inputs to the hypothalamus(4).

For thousands of years, green was an important indicator of potential food sources. As a result, it’s the only color that requires no mental processing before the brain recognizes it.
To the left of the green wavelengths are blue ones. Studies have shown these calm the mind and spark out-of-the-box thinking. On the other side, warm reds raise subconscious alarm bells. That boosts focus on tasks requiring mental focus (like proofreading or translation).

In between are plain old neutral blacks, grays, and whites — longtime corporate staples.
Summary Of Gaming Chair Color Palette Effects
Bottom line: the color of your chair only makes a small impact. In a shared office, your chair should blend with the existing office decor. At home, the novelty of any style will wear off after a few weeks. Learn more:
Psychological Chair Addictions
The world’s top-5 ergonomic office furniture brands are almost universally revered. Buying a chair from any of these mega-corps brings massive prestige via powerful brand influence.
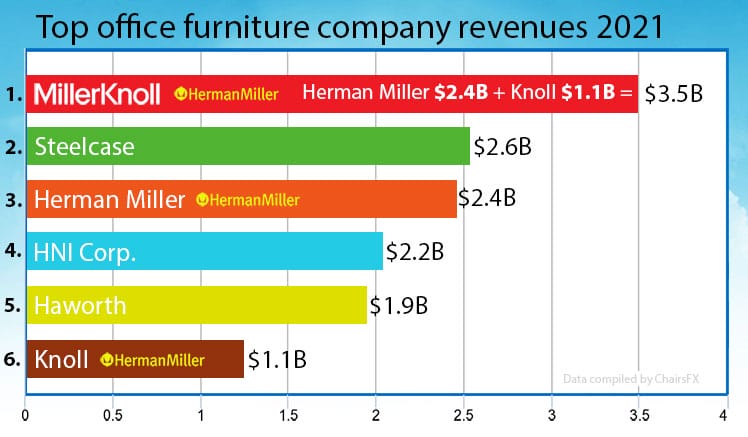
These days, the best high-end ergonomic office chairs cost between $800-$2600. Some offer such tantalizing psychological extras that users can get lost in the lights.

Without a firm grasp of physical vs psychological comfort factors, some end up buying multiple high-end chairs — but never finding comfort!

For many, the elusive search for undefined ‘comfort’ never ends! Learn more:
User-Powered Comfort Factors
Top office furniture brands are now putting out gaming chairs that support slouchier, semi-neutral postures (instead of perfect ones). Most top esports doctors will tell you that’s just fine.

Perfect posture while computing is good but unnecessary. Instead, frequent breaks and healthy lifestyles are the keys to peak computing performance. A good chair helps as a secondary support tool.
As one example, Dr. Jordan Tsai currently does performance optimization consulting for Evil Geniuses. His performance optimization priority tier places a good chair last:
Rest/nutrition/exercises > breaks > good posture > good chair. Developing healthy habits is the most important thing to work on.Dr. Jordan Tsai
In a related Twitter thread(6), he added: “Regular movement of the spine (even seated) will do far more for you than sitting in perfect posture the whole time.”
A paper from the American College of Sports Medicine(5) supports his angle. Frequent movement breaks + and healthy lifestyle habits boost computing performance more than fancy gaming furniture.

Such concepts partially explain why so many top esports teams and famous streamers are firmly atop the health and fitness bandwagon.

Frequent breaks + healthy lifestyle habits trumps all. That means you needn’t overthink the back support parts when shopping for a new chair! Learn more:
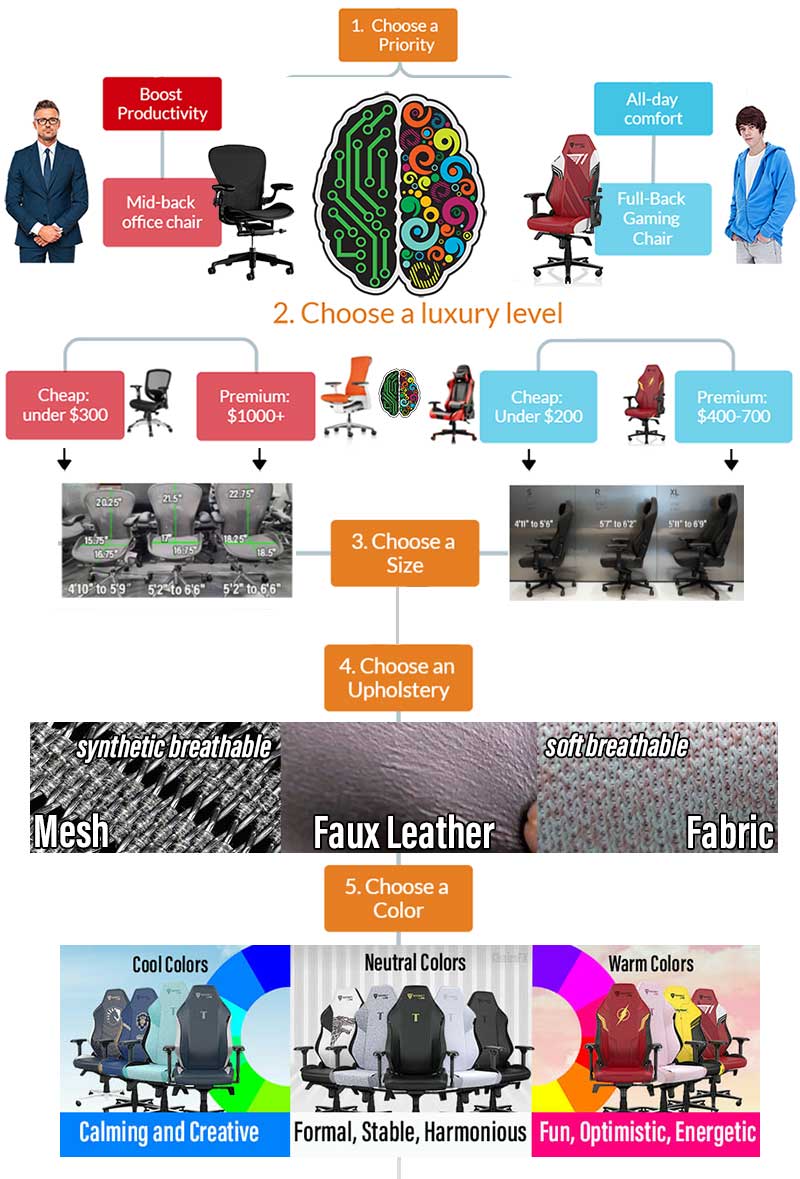
Desk Chair Picker Flowchart
Having a firm grasp of physical and psychological comfort factors will help you avoid overspending on frivolities. Then you can follow these steps to find the perfect desk chair for your needs:
Full-Back Gaming Chair Reviews (comfort) | Mid-Back Office Chair Reviews (focused productivity)
Footnotes
- Katharine Kolcaba. ‘Comfort Theory and its application to pediatric nursing’. Pediatr Nurs. 2005 May-Jun;31(3):187-94.. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16060582/, (accessed 25 September 2023).
- Matthias Rauterberg. ‘Subjective and Objective Measurements for Comfortable Truck Driver’s Seat’. Eindhoven University of Technology, 2008. https://www.academia.edu/25417370/Subjective_and_Objective_Measurements_for_Comfortable_Truck_Driver_s_Seat, (accessed 3 May 2022).
- Bianca-Michaela Wölfling, ‘Comfort Rating for Upholstery Systems’, Conference: 2nd International Comfort Congress, June 2020. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342040536_Comfort_Rating_for_Upholstery_Systems, (accessed 3 May 2022).
- Kurt S, Osueke KK. ‘The Effects of Color on the Moods of College Students’, SAGE Open. January 2014, https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/2158244014525423, (accessed 3 May 2022).
- Öztürk Gül, Elif et al. ‘The effects of achromatic and chromatic color schemes on participants’ task performance in and appraisals of an office environment’, Color Research & Application. October 2012, DOI:10.1002/col.20697, (accessed 10 Jan. 2022).
- @DrJordantsai. ‘Thoughts on Common Gaming Injuries’, Twitter, May 3 2022. https://twitter.com/DrJordantsai/status/1521201429993574400, (accessed 3 May 2022).
Anil Ramsey
I'm the ChairsFX founder and Chief Editor. I'm a member of the OSHA Education Center Association (OECA), with an OSHA Ergonomics Certification. Beyond these credentials, I've been hands-on testing the world's finest ergonomic desk chairs since 2018. Learn more about me and this website on the About Us page.
Gaming chair trends, reviews, advice.




